Theory of VROOM expectations formula and examples
- 4681
- 335
- Austin Stokes
Vroom's theory of expectations is a great contribution to the work world and organizations as it includes the importance of considering the needs and expectations of workers when structuring and organizing work activity.
In the following Psychology-online article we will explain what the Theory of Vroom's expectations, their contributions in the field of human resources and we will put some examples on the application of such theory in the field of organizations.
You may also be interested: Hawthorne effect: what is, phases and examples index- Summary of Vroom's theory of expectations
- Contributions of Vroom's theory of expectations
- Formula of Vroom's theory of expectations
- Examples of Vroom's theory of expectations
Summary of Vroom's theory of expectations
The Victor Vroom's expectations theory Explains how People act motivated by expectations that we have of the results we are going to obtain when performing a certain action. Human beings, while thinking beings and with continuous growth needs (personal/family, work and social), act motivated by certain goals that we establish for the achievement of our life projects. For this reason, the actions we carry out will come conditioned by the anticipated (or expectation) perception of the result which will derive from a certain behavior.
In this way, the behaviors that will encourage us will be those that allow us to achieve our personal goals. On the contrary, those that do not contribute anything to our personal development will be quickly discarded or, in case of being forced to carry them out, they will cause us with time a strong inner discomfort by investing our energy in actions that do not imply any type of food or Internal nutrition.
Contributions of Vroom's theory of expectations
The contributions of Vroom's theory of expectations have been given mainly in the area of social psychology and organizations, specifically in the area of human resources.
This approach has served as a basis for work planning and structuring contributing as a novelty the consideration of how the behavior of workers is motivated by the perception and expectation they have about the result they will obtain from their work action. In this way, to favor certain behaviors (performance, efficiency, etc.) or eliminate others (Absenteeism, breach of standards, delay in the entrance, etc.) The organization must take into account the aspects that will favor the motivation or de-motivation of the worker to perform them, Considering personal preferences and interests from each of them.
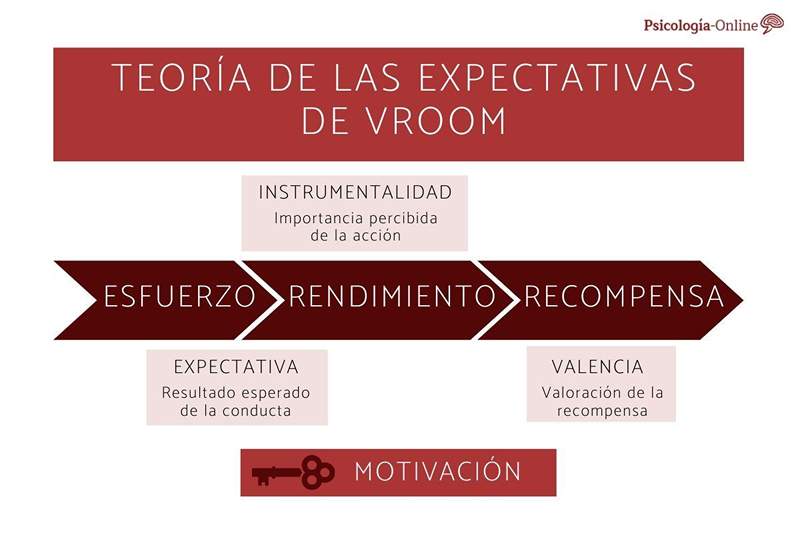
According to this theory, to ensure good work performance, it is necessary Take care of three types of relationships that occur in every work process. Since the breach of any of them will lose the motivating force towards the worker, with it, thereby negatively on his performance and efficiency. These three aspects are:
- Effort-reflection ratio: The worker's effort must be directly related to the performance he obtains from his behavior. In the opposite case (no matter how hard the expected results cannot be obtained), the worker will not feel motivated to perform such action.
- Performance-reflection ratio: In this case, it is about strengthening more the best yields, that is, at greater performance, greater reward (greater in quantity or quality, especially greater In relation to the value granted by workers).
- Reinforcement-value relationship: This type of relationship refers to the importance that the worker has to have a positive value for him To, with this, motivate your behavior.
Formula of Vroom's theory of expectations
Víctor Vroom establishes a formula to determine the degree of motivation of workers towards a certain action:
Motivation = expectation * Instrumentality * Valencia
These three factors are the key elements that will condition the motivation towards the task of the labor personnel being:
- Expectation: perception that the worker has about the result he will obtain from his behavior. Presents a value between 0 and 1.
- Instrumentality: The worker's perception that his particular action (as a constituent element of the company) will be decisive in achieving the expected result. This value also goes from 0 to 1.
- Valencia: The value that the worker gives to the result obtained by the task performed. This aspect presents values between -1 and 1.

Examples of Vroom's theory of expectations
From the formula established VROOM to determine the degree of motivation of workers towards tasks and based on the values of the different elements involved, we will comment on some Application examples of this theory in the workplace:
To favor and motivate certain behaviors
- Find out the needs and interests of workers To establish, depending on them, the rewards of the different results. The expectation of these results will motivate the action of workers. In this way, the Rewards They can range from: an increase in salary or an additional economic benefit for those most economically needy or for those who positively value money; individual or public recognition; promotion or improvement of employment; particular labor advantages; etc.
- Specify the effects that each labor action It has on the final result trying that all workers be important elements in achieving the final result. The perception by the worker of the Importance of your individual contribution will largely condition your motivation to carry it out
- Establish rewards that, as we have just said, be they important for the workers.
When the organization takes these parameters into consideration, the motivating force will be high since the values of the three elements will be positive. For example: motivation (0.72) = expectation (0.9) * Instrumentality (0.8) * Valencia (1).
To discourage and eliminate certain behaviors
This usually occurs in cases where workers perform inappropriate or disruptive behaviors. In these cases, the interesting thing is that both the expectations of the workers, the instrumentalization and the Valencia have low or negative values so that the motivating force of the combination of these elements implies a very low value that democcate the realization of the behavior in question.
For example, in the case where a worker is late for work, sanctions can be established (economic, attention calls, loss of employment and/or temporary salary, etc.) The perception of which, together with the awareness that this result depends on its concrete action, together with how negative this result implies, will demotivate the worker to perform such conduct.
With respect to the performance, if the low yields are penalized or not additionally rewarded, also the expectations of the results, the awareness of the consequences of their concrete action and the negative of the result will demotivate the labor personnel towards the low productivity.
It should be noted that this theory, like all those aimed at managing the human resources of labor organizations, must be used with responsibility and with an attitude of general improvement of each and every one of those involved. Otherwise, in not adequate hands, great abuse and labor negligence can be committed. It is therefore to encourage individual consciousness so that the benefit that these theories can contribute to us is for the benefit of global social improvements.
Another theory to take into account in the field of human resources is Herzberg's theory of the two factors on labor motivation. On the other hand, here you will find different personal motivation techniques at work.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Theory of Vroom expectations: formula and examples, We recommend that you enter our category of human resources.

