Theory of rational choice what is, history and examples
- 4751
- 823
- Glen Vandervort Sr.
A characteristic of human action is rationality and its most strictly behavioral base, intentional/conscious action. Philosophy, social sciences and economics have treated, each with their own instruments, to specify the concept of rationality and, in the case of economic theory, to make it operational.
One of the most interesting results of these attempts is the theory of rational choice. This theory, based on the neoclassical version of economic theory, represents a model of human behavior. Recently he has also found a field of diffusion in sociology. Therefore, in this psychology-online article we will deepen the Theory of rational choice.
You may also be interested: what is the theory of reasoned action and index examples- What is the theory of rational choice
- History of rational choice theory
- The theory of rational election in Criminology
- The rational model in Criminology
What is the theory of rational choice
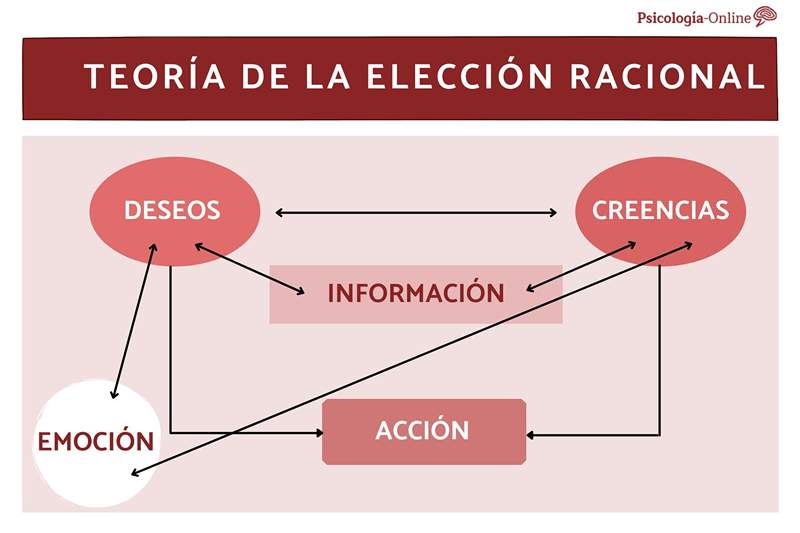
¿What is the theory of rational choice? The basic premise of the theory of the rational option is that each human behavior aims to maximize an interest Through our elections. To achieve our interests, and having certain external limitations in accounts, we will try to make the best choice to get them. A characteristic feature of human rationality itself is to maximize what we want and minimize what we do not want.
The objective of the theory of rational choice is, therefore, to explain the behavior, both individual actions and sequences of actions. According to this theory, so that the action can be rational, three optimal conditions must be met:
- First of all, the action in question You must represent the best means to perform wishes of the subject, given their beliefs. This condition implies that desires have the requirement of coherence or transitivity.
- In second place, Beliefs must be rational, that is, they must be derived from the information available through optimal inference rules.
- Third, the subject must invest a optimal amount of resources, as time, energy, or money, to gather the relevant information. The optimal investment is determined by the desires of the subject and the above beliefs on the costs and benefits that would imply obtaining more information. Decisions that are considered most important require more investment.
History of rational choice theory
The history of the theory of rational choice has its roots in the thought of economists in the 19th century. At that time, following the hedonistic and utilitarian theories, the Individual decision making It occurred depending on the desire to obtain gratification or the fear of suffering a sanction. In particular, economists, including Smith, Ricardo and Menger, insisted that the shortage of resources, which characterized the socioeconomic environment, forced individuals to make decisions.
In addition to economists, some anthropologists were also precursors of this type of ideas. Malinowski, for example, conducted studies on the "Kula exchange", a particular ritual practiced in the Trobriand Islands to demonstrate that the obligation to give, receive and correspond form a kind of reciprocity for which the exchanged objects are assimilated to the person that has possessed them, although they have no apparent utility.
The theory of rational choice made many proselytes in the sixties of the twentieth century, and then know a slight decline in the following decades. In the 1990s there was a reevaluation based on Coleman studies on social capital and electoral behavior.
The theory of rational election in Criminology
The theory of rational election in Criminology, developed by criminologists Cornish and Clarke, is the theoretical basis on which situational prevention is based. The perspective of the rational choice assumes that The author of the act, or criminal, try to get some kind of benefit out of their behavior. Therefore, the theory considers that the author Make decisions based on costs and benefits analysis about the criminal opportunities that are presented.
For the theory of rational choice, the act, criminal or antisocial, includes a decision process and the realization of elections, taken on the basis of available time, cognitive ability and information available. The premise is that the author's decisions, and the factors on which they are based, have great variability both during different phases of behavior maturation and between different types of acts.
Cornish and Clarke, give special importance to the need to analyze the different decision -making processes and decisions taken by the authors, distinguishing them by type of crime or by separating the decisions related to the different phases of participation in the act.
The rational model in Criminology
The main point of the theory of rational choice is that it considers the realization of A crime as a series of decisions and processes carried out by the author to commit that crime.
Cornish and Clarke present a real model that illustrates some of the decisions that the author will take When choosing different types of crimes. Taking as an example the theft in an apartment, the author will ask questions such as the following:
- ¿What a house is the best white?
- ¿The neighbors are monitored with each other?
- ¿How difficult it will be to penetrate the house?
- ¿What kind of objects will be inside?
- ¿How can I escape so fast?
According to this model, it is assumed that there is free will, the classical theoretical perspective, but there are some situation factors and background who can predispose someone towards crime. The background factors They can include personal skills and skills, education and personality. The situation factors may include external pressures, drug addiction and objective vulnerability.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Theory of rational choice: what is, history and examples, We recommend that you enter our personality and differential psychology category.
- « Physiological Psychology What is, History and Fundamentals
- Basic instincts of the human being what are, types and examples »

