What is the Yerkes-Dodson Law in Psychology and Examples
- 4677
- 2
- Herbert Ritchie
¿Did you know that a certain level of excitation can increase your performance and your efficiency? Although it seems absurd, when you experience a certain level of stress, your body reacts to the stimulus and can respond better in some tasks. This process is known as the Yerkes-Dodson Law or the inverted U theory.
This law, developed by American psychologists John Dillingham Dodson and Robert Yerkes in 1908, served to determine that before some physical and psychological stimuli, people are motivated more and remains more alerts. Of course, when the stimulus level exceeds a certain threshold, the effect will be the opposite. In this Psychology-online article you will find What is Yerkes-Dodson's law in psychology and Examples From this postulate that you may live daily in different areas of your life and you have not even noticed it.
You may also be interested: Thorndike effect law: what consists, examples and criticism index- What is Yerkes-Dodson's law or inverted U theory
- Why this law is known as the inverted U model
- Influential factors of the Yerkes-Dodson Law
- Examples of the Yerkes-Dodson Law
What is Yerkes-Dodson's law or inverted U theory
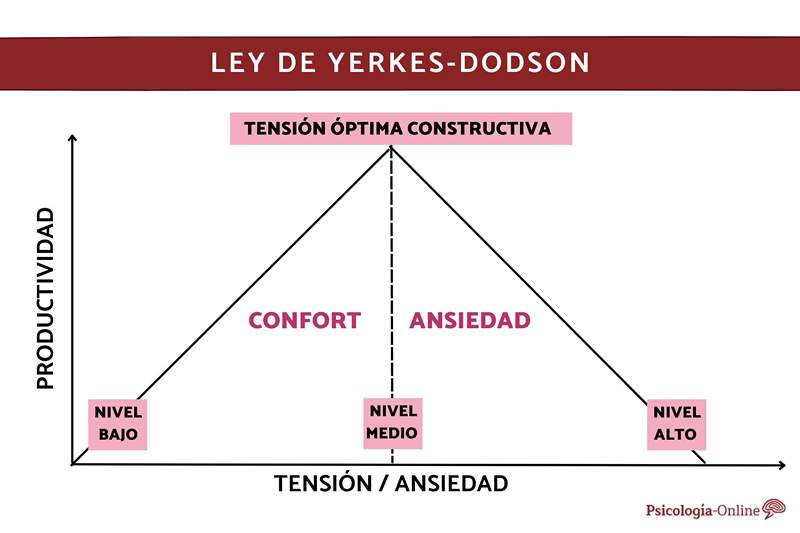
The Yerkes-Dodson Law is a theory that relates the effectiveness of the individual's stress or anxiety level. It was postulated in 1908 and intends to explain why there are different performances according to motivation degrees. This means that, The more motivated we are, the better results we will obtain. Therefore, this law is very important for achievements in some areas of life.
Was proposed following the work carried out By Robert Yerkes and John Dillingham Dodson. These psychologists discovered that through small electrical impulses, the rats responded better to get out faster from the labyrinth in which they were. However, when the impulses were very strong, the animals got out of control and totally lost the course.
In fact, when people are facing boring tasks and with a low level of motivation, it is very easy to lose interest and even abandon the activity. However, when that task becomes challenging and awakens the senses, we can focus more on finishing it. Of course, if the stimulus is overload, the stress levels rise too much and fall into a state of anxiety that limits The attention and concentration capacity.

Why this law is known as the inverted U model
The researchers who postulated the Yerkes-Dodson law, state that the excitation levels are in ascending, as if it were a bell. At the maximum point, there is the highest level of excitation that serves to The approach and motivation.
At that stage, glucocorticoid hormones are triggered to stimulate physical and brain functions; what is called as cortical activation.
From there, the individual must channel the stimulus to descend the level and relax again. In this way, cognitive functions remain optimal and improve performance and results without falling into anxiety and excessive concern.
Influential factors of the Yerkes-Dodson Law
Basically, there are 4 factors that influence the Yerkes-Dodson Law or the Inverted U theory, which we will analyze below:
- Skill levels: According to the level of skill that the subject manages, the intensity of the stimulus it requires to increase its performance can be determined.
- The difficulty of tasks: The more challenging the activity is, the greater the stimulus that triggers. Therefore, given the most difficult tasks, it is convenient to be in relaxed environments. However, if the activity is monotonous and boring, internal or external stimulation is necessary to activate motivation.
- The level of anxiety: Each person handles an anxiety trait that depends on their particular reality. Therefore, the individual's composure level before the demands, varies according to the confidence he has in his skills and abilities.
- The personality: Each individual has a particular way of responding to stimuli and perceptions. That is, it has its own personality. Therefore, you can't talk that this law also influences each person. However, some researchers, such as Hans Eysenck, affirm that those who have a more open and outgoing personality do not need as much stimulation as those that are most introverted.
In other words, the Yerkes-Dodson Law or inverted U theory will influence in a particular way according to the reality of each individual and the task to which it faces.

Examples of the Yerkes-Dodson Law
One of the examples of the Yerkes-Dodson Law is the most everyday anxiety that is experienced before An academic evaluation. In this case, an optimal stress level is needed so that performance is adequate and you can remember all the answers.
However, in the face. Together with that example, we can mention the following examples of the Yerkes-Dods law that are lived continuously:
- A football player who has prepared for the competition and before entering the court he feels motivation and enthusiasm for the plays.
- A student who will make the defense of his final work of degree to obtain an academic title will be facing a level of stress that will allow you to put your senses to the fullest to be alert.
- Sports athletes who experience a lot of excitement before each of their competitions.
In short, the Yerkes-Dodson Law or inverted U theory can be applied in different areas of life, not only to increase performance, but also to recognize when it is necessary to stop and take a break.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the Yerkes-Dodson Law in Psychology and Examples, We recommend that you enter our category of basic psychology.
- « When you can break the professional secret of the psychologist
- What is a psychoanalyst and what does it do »

