Nociceceptors what are, types, location and functions
- 3995
- 744
- Ryan Bogisich
In addition to the typical typing receptors, somatic sensations depend a lot on the nociceptors, arborized free and non -myelinized nerve endings of nerve terminals, which indicate that the body's tissue has been damaged or could be.
The information of the nociceptors follows a path to the brain that is widely different from the one taken by the typositive typositors. Consequently, the subjective experience raised by the activation of these two ways is different. In fact, selective activation of nociceptors can lead to the conscious experience of pain. In this psychology-online article, we will see together What are the nociceptors, the different types, their location and functions.
You may also be interested: Encephalins: What are, function and index types- What are the nociceptors?
- Types of nociceptors
- Location of the nociceptors
- Functions of the Nociceceptors
- Difference between nociception and pain
What are the nociceptors?
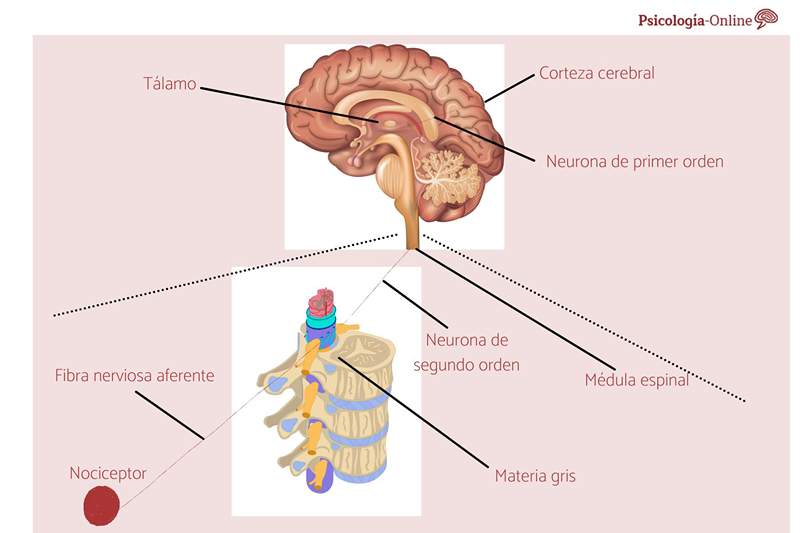
The word nociceceptor derives from Latin nocere and means damage. Thus, the nociceptors are sensory neurons endowed with sensitivity to painful stimuli. Nociceptive neurons have their cell body within the spinal ganglia of the dorsal roots located near the spine. In this article, you will find information about the types of neurons, their structure and functions.
¿What are the nociceptors? These neurons are typical T cells, since they have a direct branch on the periphery, responsible for the transduction of the painful stimulus, and a branch that is directed centrally and establishes synaptic contact with the neurons of the superficial sheets of the dorsal horns of the spinal cord.
The neurons of the spinal ganglia mediate the sensitivity to pain from all parts of the body, except the facial district. This is covered with nociceptors located at the base of the skull, specifically, in the trigeminal nuclei. The nociceptors send their Skin endings, the muscles, The joints, Meninges and deep somatic tissues.
Types of nociceptors
Nociceceptors can be divided according to their functional properties. Let's see what are the types of nociceptors:
- Mechanical nociceptors: They respond to intense skin stimuli such as pinches, punctures or crushes. Give a feeling of living pain. The signal is collected from nerve endings and transported to the central nervous system by myelinized fibers called toδ. The driving speed is between 5 and 30 meters per second.
- Heat nociceptors: Examples of nociceptors that are excited by extreme temperatures above 45 ° C or less than 5 ° C. These temperature sensitive nociceptors also transmit the signal through myelinized fibers toδ.
- Polymodal nociceptors: They are activated by a variety of stimuli that can be mechanical, thermal or chemical signals. Produce a sense of deaf pain. These lead the signal to the central nervous system by non -myelinized and low diameter f fibers. The transmission speed less than 1 meter per second.
- Silent nociceptors: They are present above all in the viscera and are relatively insensitive to the stimuli that can be perceived by the cutaneous nociceptors. On the contrary, also called visceral nociceptors are sensitive to torsion, distension and ischemia of an intestine. They generally have broad and superimposed reception fields.
The different types of nociceptors often act in a coordinated manner in the reception of the Dolores signal. For example, as a consequence of a harmful, mechanical or thermal stimulus, the activation of myelinized fibers toδ He is responsible for an initial, sharp and localized pain. This pain is followed by a more widespread and persistent one generated by the arrival of the stimulus of the f fibers.
Location of the nociceptors
Nociceceptors are free nerve endings of the corresponding peripheral nervous system, which selectively respond to different chemical, mechanical and thermal stimuli. The nociceptors They are distributed throughout the body, But not uniformly. Therefore, Pain sensitivity differs according to its position.
The variability of nature and location of nociceptors influences pain sensitivity in different areas of the body. For example, the number of nociceptors in the fingertips is greater than that of the skin of the back and, in addition, the entire surface of the skin has more nociceptors than the internal organs.
Functions of the Nociceceptors
The nociceptors participate in the general sensitivity system, more specifically they carry out the Noceptive or Protopathic Function. Let's look step by step how it develops:
- The stimuli produced by harmful agents for the physical integrity of the body cause unpleasant sensations such as pain, excessive heat or excessive cold.
- These sensations alert the individual and raise defense reactions to remove the harmful agent.
- The sensations of pain and heat of this type are delayed with respect to the stimulus, persist after their cessation and are not localizable.
Difference between nociception and pain
It is important to be careful not to confuse the concepts of nociception and pain because they are not always the same ... Next, we will see the difference between nociception and pain:
- Pain: sensation or perception of irritating, exacerbable or unbearable sensations from a part of our body. The pain can be intermittent, however, the following opposite statement is also true: pain can be unbearable, even without a nociceptive activity.
- NOCICEPTION: sensory process that provides the signals that then locate the pain. Nociceceptors may be acute or continuously active. To a greater extent than in other sensory systems, cognitive qualities of nociception can be controlled from the inside, that is, by the brain itself.
In the following article you will find more information than and how we feel pain.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Nociceceptors: What are, types, location and functions, We recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.
- « Nervous System Development Stages and Factors
- Prefrontal cortex what is and what functions it does »

