Motivation to achieve your goals

- 2488
- 186
- Miss Drew Stroman
As with any human dimension, motivation is difficult to define and much more to guide. Let's think of these three theories: the rationalism traditional, which considers that we act because we have a reason to do so, thus being responsible for our actions, the mechanism which would be the opposite: we act due to biochemical factors that would understand our performance if we improve our performance. And you can't miss the Empirical determinism that comes to tell us that our behavior has happened when specific conditions are met, the latter aligns more in the effects derived from learning,
The motivation is formed by many factors such as our personality, the basic instinct, learning, expectations, physiological states, etc. The undoubted thing is that it is a necessity or a desire that energizes our behavior and directs it towards our goal.
Content
Toggle- Motivation and emotion
- The origins of behavior
- Primary and secondary motivations
- Maslow's pyramid
- Need for achievement
- People's styles with a great need for achievement
- Affiliation and power needs
- Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations for motivation
- To increase your motivation
- References
Motivation and emotion
Closely linked to it, there is emotion and that is that the two stimulate a certain behavior. Emotion is that positive or negative feeling that follows a physiological activation (crying, fear), and behavior accordingly, that is, motivations are accompanied by emotions, an example: I have a great motivation to go out with my classmate@ of work that I like, and this right now brings me emotions such as joy, fear, love ..
On the other hand, emotions usually have a motivational component in them postpone other commitments, etc.
The origins of behavior
We want that job, they have already given us the interview and in the end we miss. We have gone to the nutritionist and we signed up for the gym and suddenly we leave the Chinese of the corner. We read the newspaper and the first news is that the husband who has just murdered his unfaithful wife is considered guilty. What happened?, Why do I miss the interview that could improve my professional area?, How do I think of going to give a “feast” after having committed myself and being following a diet and new lifestyle?, Why does the husband come from his wife in the most cruel way?
Each and every one of these behaviors have traveled many paths, accentuated by the primary impulses and nuanced by learning, physiological imperatives, the need to explore and dominate the environment, those expectations, the anxiety that activates or blocks motivation and our personality.
 How to change a habit: the 6 stages of behavior change
How to change a habit: the 6 stages of behavior change Primary and secondary motivations
Many of our motivations come from the need for survival: thirst, hunger, sleep, breathe, maintain body temperature and of course, sexual need, these are Primary motivations And they regulate homeostatically, that is, they seek balance at all costs.
The need will create an activation, consistent with the intensity of the reason, which in turn is aimed at reducing the impulse. The most dependent are biological needs, but the rest of impulses are not necessarily marked by lack, they can be stimulated from abroad, that is, through environmental incentives that are able to activate our behavior,
The Secondary motivations They are those that do not meet a biological need, they are called acquired because learning and culture influence among other things, they are of more social type.
It is possible to motivate if something produces a reward or punishment, for example sports hobbies, professional vocation, social status desire, etc.
Maslow's pyramid
In 1970, Abraham Maslow proposed a hierarchy of the motivations that today is still perfectly valid:
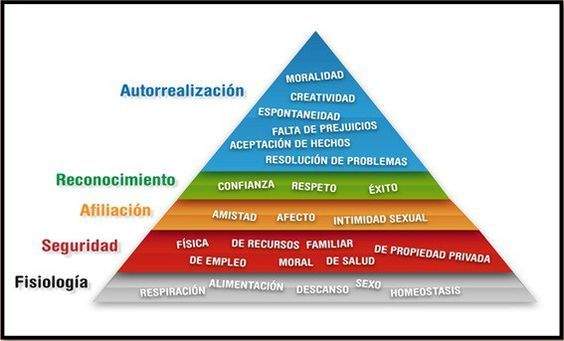
Maslow's theory of human needs: how to achieve self -realization?
As we see here, our interests are ascending from the base, which would be the physiological needs, through security, belonging or affiliation, love, recognition and reaching self -realization, which includes the most transcendental of us, the development of our own nature in all aspects.
As a general rule and analyzing it multidisciplinarily, you cannot concentrate on your work or studies if you are not insured your livelihood or are about to dislodge your home. In any case, the order of needs is not universally demonstrated again, individual differences come into play.
It is possible that adult behavior follows mainly to reasons that have reached full autonomy against any need for biological order, that is, they become habits, for example: we order our things because we receive praise or punishments, but after constantly practicing it, the order ends up being a desired behavior. In other words, depending on instrumental learning we can condition our interests.
 Need for achievement
Need for achievement
Think for a moment in you, do you try to succeed, to highlight the objectives that have been set?, Or do you think of yourself like an@ abúlic@, conformist or excessively disciplinary?, Well, if you lean more about the first question you are greatly motivated for one of the most common impulses of our society: obtaining achievements, of achieving a significant result and of improving your tasks.
People's styles with a great need for achievement
- They tend to prefer moderately difficult tasks that allow success, since it will be attributed to their own effort and skills.
- They fit a high self -control and are persistent
- They are willing to spend their time to the achievement of their goals.
 Individual differences come from the personality structure of each one, some of us direct our impulse to the achievement of success and to avoid failure. Being then more susceptible to the prize or punishment, in addition to the enormous importance of educational models and cognitive anchors that are learned from childhood.
Individual differences come from the personality structure of each one, some of us direct our impulse to the achievement of success and to avoid failure. Being then more susceptible to the prize or punishment, in addition to the enormous importance of educational models and cognitive anchors that are learned from childhood.
 50 phrases of Desmond Tutu, theologian and pacifist
50 phrases of Desmond Tutu, theologian and pacifist Affiliation and power needs
Other typical motivations are those of affiliation and power, but sometimes we confuse them with the achievement.
As a summary, the former refer to the concern to establish, maintain and restore friendly relationships, and the second to concern for reputation, influence and shield To others.
Intrinsic and extrinsic motivations for motivation
The motivation that arises within ourselves, for example the desire to learn to know, that need to do it well for one's satisfaction we call it intrinsic. The extrinsic It is stimulated from abroad through rewards, for example, extra bonds, the sweet that is given to the child, etc.
The most powerful is undoubtedly the intrinsic, so, if you can give a more transcendental sense to what you do by obligation you will surely feel more motivated and content@
To increase your motivation
50 best motivating phrases for success
References
- Bermúdez, j., Pérez-García, a. M., Ruiz Caballero, J. TO., Sanjuán, p. and wheel, b. (2012). Personality Psychology. Madrid: UNED.
- Count Pastor, M., Rivero Expósito, M. P., MENÉNDEZ BLAZA, F. J. and Sanz Aparicio, M. T. (2013). THE PSYCHOLOGY OF MOTIVATION. Madrid: Sanz and Torres Editorial.
- The motivation (2007).In Encyclopedia of Psychology. (Vol. 2, 35-57 pp).Spain: Ocean.


