Fears, anxiety and phobias differences, normality or pathology?

- 4242
- 1291
- Gregory King
Mother: ¡I don't want to go to school, my head hurts a lot, my triplet hurts a lot!
Mother: ¡I want to sleep with you, I'm afraid! ¡Do not turn off the light! ¡Do not leave me alone!..
Mother: ¡To the house of the yayos not that I am afraid! ¡Do not go! ¡Relief a dog, a spider!.. ¡I can not drive! ¡I can not eat! ¡I can't enter the elevator! ¡I can't go to the theater! ¡I can not leave home!..
Fears are normal experiences in children's life. Given the need to put light on this subject, in Psychologyonline, we offer this article about Fears, anxiety and phobias: differences, ¿normality or pathology?.
You may also be interested: fear of darkness in children: causes and index treatment- Fear in emotional response
- Anxiety as a psychophysiological response
- Phobias as an uncontrolled and disabling response
- Different hypotheses about the origin of fears
- Most common fears in childhood
- Most common fears in childhood II
- Specific phobias
- Social phobias
- Agoraphobia
- Therapies
- recommendations
- Attitudes that can prevent the appearance of phobias
- 10 rules to face panic
- Final reflection
Fear in emotional response
Fear is a normal and universal, necessary and adaptive emotion that we all experience when we face certain real and imaginary stimuli, children throughout their development will suffer and experience numerous fears: to separation, strangers, strong noise, to darkness, to fall alone, to animals, to school and so we could continue with a very long etc. Most will be passengers and will not represent any problem, They will appear and disappearing depending on age and psychoneurological development.
These fears, through learning, will be very useful on many occasions They can help them to face properly and adaptive to difficult, complicated, dangerous or threatening situations that may arise throughout their lives and Their fundamental function will be to protect them from possible damage generating emotions that will be part of its continuous evolution and development (the child should not be afraid of the slides for eg., but it must be prudent when they go down and play in them).
Therefore it will not only be normal but also necessary for children to experience specific and concrete fears In situations, objects and thoughts that involve real danger or threat, thus avoiding running potential unnecessary risks that can jeopardize their life, health or physical or psychological well -being, but without these being important enough to significantly alter their life or cognitive or emotional development.
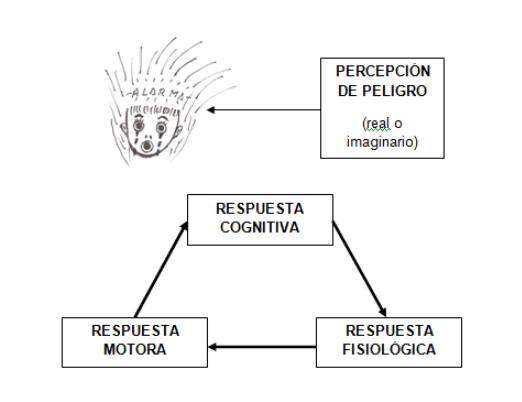
Anxiety as a psychophysiological response
Anxiety is a psychophysiological response of alarm that arises when the person needs to react to certain situations, stressful events or stimuli perceived as threatening, dangerous or uncertainty, whether real or imaginary, internal or external. Like fear, it is also a normal, necessary, adaptive and even positive response because it prepares the body to mobilize in situations that require a neuronal activation superior to that required by many other situations that do not imply any difficulty.
While the alarm status lasts or alert, the agency launches a whole series of defense mechanisms, both physiological and psychological, in order to overcome and face the possible threat and although during this time the feelings, not pleasant, of anguish and insecurity also increase also also greater perception of the environment is increased and greater acuity and mental concentration In addition to better physical preparation to facilitate that the confrontation to the threat can be carried out as successful as possible and we can even increase our performance Whenever the Ansiógena response ends as soon as the anxious disentent factor ends.
Fears considered normal and dependent on maturation development:
0 to 1
Fear of strange or violent stimuli, given the loss of support, to the strangers, to the separation of the parents… (They are considered genetically programmed and of high adaptive value because they will help us survive before possible threats or dangers)
2 to 4 years
The evolution of authentic children's fears begins, Most fears of animals begin to develop at this stage and can last until adulthood. We are afraid of falls, animals, strangers, strong noise, darkness, cars, separating from parents, changes in the environment, masks ... (the child can explore their environment so fears are increasing because there is more likely to encounter danger situations, Avoidance responses appear When fleeing from the frightening stimulus and running to the encounter of the parents) (the nature of fears and cognitive development also changes so that fears are taking a more social character and the usual thing is that they disappear progressively as the child grows and face them)
4 to 6 years
The fears of the previous stage are maintained but The stimuli that can potentially be able to generate fear are increasing as, strong or strange noises (sometimes the product of their imagination), thunder and lightning, to bad people, to changes in the environment, to the masks, to the heights, the catastrophes, and the imaginary beings (monsters and ghosts), to bodily injuries, to sleep alone or stay alone .. The child's cognitive development and their fantasy capacity are at these older ages Therefore, imaginary stimuli enter, the most varied situations and diverse phobic stimuli are added that can last until adulthood.
6 to 9 years
The child reaches the ability to discriminate the internal representations of cognitive reality. Fears will now have greater realism and will be more specific, the fantastic world and fear of imaginary beings will disappear but little by They will take more relevance more specific and concrete fears As fear of darkness, physical damage and wounds, criticism or ridicule due to the absence of school and sports skills, school, school failure, animals, to be observed, to the physical aspect, they also increase The fears transmitted by the media .. Little by little they will disappear some fears and increasing others depending on how small clashes have passed that they have been presented throughout their short life.
9 to 12 years
As in the previous stage Cognitive reality is taking greater relevance, They begin to become aware of concrete and specific fears but more based on objective reality As fear of fires, thunder and lightning, exams, academic performance, school failure, bodily injuries, accidents, contracting serious diseases, death, the sense of ridicule increases, it appears The fear of serious conflicts between parents (fights, separations, divorces) or poor school performance, the fear of classmates is increased and especially those who are aggressive. At these ages it usually gives a slight rebound of fears that seemed overcome.
12 to 18 years
In this stage fears to animals and concrete stimuli are reduced To be giving step to fears related to personal self -esteem (intellectual capacity, physical aspect, fear of personal or school failure) and social relationships (Concern for rejection or recognition from their peers, classmates ...), to criticism ... at this stage Family distancing begins and the need to experience new risks As a form of self -affirm within the group of friends, little by little they will leave the children's stages behind and take prominence of the membership group.
From 18 years
The fears will evolve due to learning, to their own or witnessed experiences in foreign people, Some will be necessary and adaptive They will help us to be on a warning and caution in the different situations that may require it and we will strengthen, others will overcome without leaving any mark but others will derive in authentic phobias With all the consequences that can be derived from it. Hence it is fundamental to prevent, resolve and acquire the necessary resources and skills to be able to face and respond satisfactorily to the environment both internal and external and prevent a fear that in principle is adaptive to end up deriving in a phobia that is no longer adaptive but pathological.
Phobias as an uncontrolled and disabling response
Fear and anxiety cease to be normal, adaptive, necessary and positive responses when They exceed the tolerance threshold, There is no control of control, continuous avoidance of the aversive stimulus occurs, they interfere considerably in the normal and adaptive functioning.
The answers are still maintained despite the amount of rational explanations they may receive in this regard, then Terror incapacitates them to listen to reasons or make rational decisions In real or imaginary situations or before objects and animals that for most people do not represent any danger except for whom their brain interprets them as terribly dangerous and threatening. These answers are excessive And they are loaded with a considerable and persistent state of consistent anxiety, are unreasonable and intensely disproportionate, They extend over time and generate clinically significant discomfort With enormous suffering, which the child and the parents or adults who take care of him suffer, presenting a set of symptoms that can be disabling for the person who suffers them generating all this a state that escapes the control mechanisms.
In this situation, fear becomes a phobia, where There is no fear but panic, And anxiety ceases to be positive to become negative and pathological which makes it highly harmful and harmful to whoever suffers it in addition to significantly altering their ability to face everyday situations (such as sleeping, being alone or with people, going to school, leaving home, traveling, facing different situations that will depend of the feared object, etc. and ultimately to lead a normal and satisfactory life).
Establish the border between fear, anxiety and phobia will not always be easy It will depend on factors such as age, nature of the feared object or situation, frequency, intensity, degree of incapacitation, etc.
Before a phobia, behaviors of the most disparate and with great difficulty in maintaining rational thought will be presented, reacting from absolute immobility to panic attack where the norm is the Great avoidance of the aversive stimulus or with one Desperate and without control escape when you cannot avoid and there is no choice but to expose itself to the same.
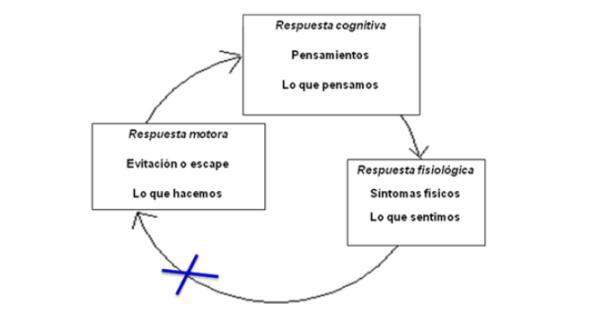
To better understand what happens before a phobia we can analyze the manifestations through three levels of response: The physiological, the engine and the cognitive.
Cognitive response
Refers to all thoughts, beliefs and images all with a great danger or threat content and that derive from the fear perceived before the phobic stimulus. These thoughts are automatically produced with total perception of loss of control, great conviction that it cannot be supported, that the worst will always happen with great anticipation of all types of disasters .. The anticipation will be totally negative and even with a long time in advance. In general we will meet:
- Large amount of subjective anticipations related to physiological reactions
- A lot of erroneous, negative and irrational beliefs regarding the feared situation
- Great physical and mental tiredness
- Difficulties of attention, memorization and mental concentration
- Altered space-time perception
- Unreal, distorted, very negative and catastrophic thoughts
- Feeling of unreality, sadness and great disinterest in the environment
- Feelings of failure and disability of coping
- Fear of dying, to suffocate, to suffer a heart attack, to suffer an accident, to lose control ..
Physiological response
Includes all internal manifestations That we can feel when we are facing the phobic stimulus, the sensations will vary from one people to another depending on the type of phobia, which for some will be fundamental to others can be irrelevant. A person who is afraid of suffering a heart attack will be dreadful to palpitations, tachycardia, chest pain or arm ... while a person who is going to eat in places he does not control, so it may happen to him, he will not endure small inconveniences Abdominal, feeling of choking, nausea ... Among the most common physiological manifestations we can find the following:
- Heart rate acceleration, palpitations
- Intense thoracic oppression, pain or chest discomfort
- Feeling of lack of air, drowning, choking
- Excessive sweating
- Dry throat and mouth
- Urgency of urinating and defecating
- Tremors, paraesthesia (numbness of members or tingling sensations)
- Difficulties to sleep
- Muscle pain, head, abdominals ..
- Gastric acidity
- Digestive disturbances (diarrhea or constipation, nausea, vomiting)
- Feeling of dizziness, vertigo and even loss of knowledge ..
Motor response
Includes all those Behaviors for avoidance, escape, to search for help and security, isolation, to perform anything that allows them to get rid or escape from danger... Some will go to the emergency room before the minimum physiological manifestation, others will not leave the house without carrying with them anxiolytic or the drugs that provide them with the necessary security, others will avoid activities that imply physical effort, others will not eat certain meals, others will be unable to stay alone, to speak in public, to relate, to ride by car or any other means of transport ... each one will avoid everything that is to a greater or lesser extent related to their phobia. In general, we will find:
- Total avoidance of the feared object
- Isolation or attempt to be surrounded by people who increase security
- Urgency for escaping, fleeing with total loss of control
- Irritability, anger, aggressiveness, uncontrolled movements
- Shout, cry, block with great motor inhibition ..
These three responses the cognitive, the physiological and the motor will always be found present and intimately interrelated when an abnormal state of anxiety is activated. That is why we modify any of them, we will automatically modify the other two, so it will be vital to know them thoroughly to be able to expose and face the vicious circle in which the person suffering from a phobia is hooked.
In addition to what is commented, We will also find biochemical changes as greater secretion of adrenaline, norepinephrine, fatty acids, corticosteroids ... and ultimately with a nervous system willing to generate everything necessary to deal with the needs of confrontation, fight, escape or, where appropriate, return to normal. Due to sensory impulses (coming, for example, of the eyes) Neural networks They detect danger, They are activated and They give the signal of "Alarm" which is transmitted first to the thalamus. If he Tálamo and la Ampigdala (brain emergency central) They consider the stimulus as dangerous, They automatically launch the general alarm and fear, rage or any other emotion go on stage and extends in tenths of second throughout the organism through brainstem which causes different physiological changes in the organism that They prepare it to face the danger either real or imaginary.
- The heart and breathing accelerate, Increase heart rate and blood pressure. Getting that the muscles receive more blood, to eliminate more toxins and facilitate flight or defense while more oxygenation.
- Skin blood vessels narrow to flow through them less blood and benefit above all internal organs.
- The immune system mobilizes additional defensive cell battalions To face the consequences caused by the threatening situation.
- The adrenal glands activate adrenaline release that is responsible for brain and muscles have an additional energy contribution.
The body is ready to run away. Once overcome this first reaction phase The sign of "Danger" arrives to the cerebral cortex where the Conscious thought and That's where the situation is really analyzed. If the brain Through thought also qualifies the signal as "danger" (for example, a threatening situation for us) The reaction intensifies. And it is from this moment When the hormonal race begins through the brain and all over the body. The goal is again in the Kidney glands that Now they are going to segregar cortisol. This hormone Body reaction exacerbates even more and It will be in charge among other things, to maintain the answer mobilizing enough reserves so that the energy supply is adequate. Later, after the perception of danger, it will be Cortisol himself who is in charge to give the stop sign And that the system returns to its normality situation ending the situation.
The function of all these changes will be to be safe When we are facing a real danger because in addition to mobilizing to avoid it, fleeing or seeking help, it will also learn to avoid in the future those similar situations that really represent a danger. The problem will arise when the alarm reaction is launched uncontrolled and without a real danger that supports it. In this case It will be the person who starts the entire system of alarm When interpreting the situation as dangerous Based on sensations that he experiences or perceives as such for the mere fact of thinking that he is facing a danger regardless of whether it is real or imaginary.

Different hypotheses about the origin of fears
As we see fears are very common and in principle Although almost all children feel anxiety and fear at some point in their lives, these fears are normal, They appear without apparent reasons, they are subject to an evolutionary cycle and usually disappear over time as the cognitive, social, maturative or emotional characteristics evolve, except for the fear of strangers that can survive during adult life giving more intensity in the most intensity in the cities that in the villages, where almost everyone is known and the perception of danger to strangers is of less intensity. We will only worry when they interfere with everyday life And it must be an expert who determines whether it is fears inherent to evolutionary development or on the contrary it is a problem that must be solved to avoid future problems.
Through numerous investigations it has been revealed that girls usually present more fears and more intensity than boys.
There is several hypotheses about it as the biological according to Men would be better endowed for attack and defense showing less fearful behaviors to be constitutionally stronger.
The Sociocultural whose explanation would be given by The differences determined by the social roles transmitted to each sex depending on the social environment in which it develops. Girls have greater permissiveness in externalizing feelings and emotions related to fearful situations. Girls are not required to be brave or face risk situations with the same intensity as boys “the fearful girl is most easily understood than the child, there are signs of affection and understanding when he feels fear, to the Child, on the contrary, it is required to be the strong, the launched, the one who faces and the more courage confrontation to fear.
Now each depending on their personal characteristics or their own experiences will develop or not different fears that can lead to phobias But regardless of genetic programming to develop normal evolutionary fears that play a clear survival factor, of individual or sex differences we also find with multiple factors that can influence the development of phobias such as family patterns This hypothesis would explain the phobias based on behaviors learned by the observation of models "Modeling learning" (especially through parents or relatives). Feedful parents could be unintestrately, through their behavior and emotions, inductors to establish different fears in their children "fearful parents will transmit to their children insecurity and fears".
On other occasions it will be a consequence of the direct or indirect experience, A child or an adult who has been bitten by a dog, or has seen how a dog has bitten another person, it is very likely that dogs experience dogs and even for generalization extend to other animals, on other occasions the uncontrolled fears will come determined by verbal instructions coming from the environment as a way of controlling behavior (What comes the coconut, the man from the bag will come and will take you, if the Pirula Witch will come badly and take you to his cave ...) or by the media or through films that are presented as threatening or terrifying and even the cartoons themselves will be caused to generate different phobias in children. On other occasions in our mood to provide protection we will do it overprotecting excessively and preventing that they may face normal or complicated situations that allow them to develop their intellectual curiosity, resources and skills to face them or enhance independent and responsible behaviors.
Other times will be the Unpleasant or traumatic vital experiences After witnessing ill -treatment, fights, serious accidents, deaths of a love.
On other occasions they will be Fruit of imagination or misinformation Given certain physical diseases, many times we will be adults themselves who will use fear to protect children in potential real and dangerous situations (electrical plugs, traffic, animals, go alone down the street, contact strangers ...) ..
In short we see that The origin can be diverse and multifactorial causes, It will depend on how we act in this regard, on how we anticipate or face the feared objects, how we solve, to do it with greater or lesser reheating, that we acquire greater or lesser number of resources and confrontation skills... the one who stays at all and disappears without leaving any sequel and we can even be strengthened from it or on the contrary becomes an authentic clinical picture with greater or lesser pathological complication.

Most common fears in childhood
Fear of separation
It is one of the first fears to appear. It is characterized by intense fear of being far from parents, family or people emotionally linked to them, it is a highly adaptive fear and with a great survival value, in fact their presence indicates a certain degree of maturity in the child. Practically all children when they are young. Its resolution will not represent any problem and will generally do it without leaving any mark. When solving the problem, parents will play an important role because parents who express great anxiety about the separation of their children will end up infecting them. Hence, the type of parenting is essential for children to pass this stage without suffering major damage and can move towards increasing autonomy.
Newborns show crying or altered behavior when they are hungry, they are tired or uncomfortable without this implying fear itself because it is simply an alert call in search of protection and therefore a highly adaptive reaction because it helps them survive before possible threats. It is 6 months when babies begin to express the anxiety that generates the separation of their parents or the people who take care of it through tears and screams, Fear will be more specific when children begin to walk and they will express him running towards their parents as soon as they perceive departure from the people who protect and care.
The child who suffers from this disorder feels a great discomfort when he is or thinks he can be found alone before any type of threat. Anxiety can become so great that the child refuses to sleep alone, to stay alone, to go to school ... even presenting night nightmares related to physical separation or symptoms such as headache, belly, stomach ..
The normal thing is that it solves without problems as the child grows But if not satisfactorily resolved, its early detection that will be determined by the degree of anxiety manifested will be fundamental, since it has been possible to verify its close relationship with the school phobia in children and with agoraphobia in adults.
Fear of strangers
It is an innate and universal fear. Its appearance occurs between the first and second year of age and is the most feared stimulus between six months and two years.
Before a stranger the child will respond by diverting his gaze, breaking to cry or shouting and the answer will depend so much on the situation (that the child is alone or accompanied by parents or caregivers, that the situation is more or less known ...) as well as the behavior of the stranger (that is slowly or unexpectedly approaching, there is or not physical contact ...) or the physical characteristics of the stranger (women cause less fear than men and children less than adults). The previous experience with strangers will also play an important role, It will be easier and will represent less fear for those children accustomed to relating to different people than those whose relationship is more limited to the family.
Will tend to refer as we mature both cognitively and emotionally.
Darkness
It usually appears around two years and generally disappear towards nine. It can produce great anxiety at night and especially at bedtime, causing great discomfort and fear of sleeping alone or being dark, it is usually associated with different types of fears such as monsters, witches, thieves, hidden imaginary beings that They can appear at any time ..
The fear of darkness, Sometimes it will be accompanied by sleep disorders such as nightmares or night terrors. Both will occur during sleep but present very different characteristics, Nightmares usually appear between 3 and six years of ageThey are characterized by presenting a content loaded with great anxiety that will remember clearly when they wake up once the dream is finished, however In the case of night terrors, the awakening will be abrupt, it will be accompanied by screams, crying, open eyes and great manifestation of confusion and disorientation, without the child responding to the parents' efforts to awaken him and without remembering anything that happened to the wake up once the dream is finished, It usually occurs between four and twelve years of age And it represents a great alarm for parents who see how the child presents these manifestations without them being able to do anything to help him. Unlike nightmares the child will not remember anything.
School fears
The school is the place where children spend most of their time and where a large number of experiences both positive and negative live. Fortunately it affects a minority of children and It tends to occur between 3-4 years or 11-13 years although it can also occur outside the mandatory studies. Its beginning in children is usually sudden, while in adolescents it is presented more gradually, with greater intensity and with a worse prognosis. The phobia to school It is preceded or accompanied by physiological symptoms of anxiety (tachycardia, sleep disorders, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache or guts, great discomfort ...) and with great cognitive anticipation of highly negative consequences associated with everything related to school as well as great dependency towards the mother or caregivers. All this will increase the behaviors of avoidance, disability, inhibition and blocking towards school tasks with all kinds of anticipatory anxious behaviors. Unlike what happens with other fears, It has been proven that the school phobia increases with age, Hence, if school failure is not fought on time, in addition to increasing many other associated fears such as fear of the teacher, school failure, to make a fool of them, to read aloud, to make mistakes, to which they laugh Of these, to the classmates, to the social relations ... what will considerably reduce their safety and their self -esteem with the risks that all this entails.
Among the most typical responses that we can find, among others, the following:
- They refuse to attend school inventing a thousand excuses and delaying their departure everything they can.
- They cry, shout and kick when the time comes to go to school and if they go to school they cry and grab their mother hard so that they do not leave them.
- They complain about all kinds of headaches, gut, legs ... with a great variety of physiological symptoms such as tremors, leg stiffness or arms, excessive sweating in the hands, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea ... when the time to go is approaching to school but disappear if they are allowed to stay at home. During the weekend or on vacation nothing hurts them, they are happy and they are great.
- They anticipate all kinds of negative consequences, which predisposes them to give highly unfavorable answers which considerably increases their fear of confirming their suspicions.
- They carry out a very negative self -assessment of their capabilities which greatly hinders their learning.
- They plan all kinds of escape and avoidance responses ..
The phobic response, in this case, is maintained and persists for the benefit obtained by avoiding the phobic object that in this case will be the school with everything that accompanies it: reduction of school tasks, greater attention received, performing substitute activities Much more pleasant, with the excuse of not finding themselves well they can stay at home playing, watching TV ..
Before these fears it will be essential to act as soon as possible, Before they can lead to a phobia, to provide them with enough resources and skills to face the different anxious situations that will appear throughout the school process and thus avoid or hinder the appearance of future emotional disorders, failures School, social or personal.
Most common fears in childhood II
Fear of dogs, cats or other animals
In this case, animals will be the cause of fear or possible phobia And as the cause of fears we will find dogs, cats, snakes, spiders, rats and mice, flying insects and birds as more frequent, reaching the maximum anxiety point when animals are in motion. In some cases it will be acquired through direct experience but on many other occasions it will be transmitted through the different models that have experienced a phobic anxiety against certain animals. Interestingly, many do not believe that the animal hurts them, because sometimes they have never seen them, but they are convinced that they will be terrified, that they will lose control, that they will suffer some mishap when trying to escape or will have a cardiac arrest, or will never endure The feeling of disgust or disgust that may cause their presence or anticipate so many disasters that will avoid by all means approach both in an imaginary way.
The fear of animals will be given above all in childhood and will generally have a transitory character, but there will be occasions in which it derives in a real phobia and translates into a significant deterioration of everyday activities (Resistance to go out for fear of meeting a dog, a cat or fear of performing certain activities where the feared animal can be crossed ...) depending on the feared animal, because for example it is more difficult to cross with a snake than with A dog or with a spider, the person will experience greater or lesser inability to carry out a normal life, and this will be decisive to take appropriate measures when making the decision to go or not to a professional who helps us overcome The phobia.
Fear of disease and physical damage
It is a universal and highly adaptive fear because it represents a real threat to the safety and survival of the human being.
The fear of wounds and blood occurs in almost all children although it will prevail to a greater or lesser extent based on previous experiences lived by themselves or transmitted by relatives who present phobia both to blood and physical damage and to real or imaginary diseases. Accompanying the phobia, symptoms can be given such as respiratory difficulties, tachycardia, dizziness and even fainting ... fears of doctors, dentists (quite common especially in men, great hypersensitivity is presented to the drowning reflection when objects are introduced into the mouth or The throat is pressed. In severe cases, the drowning occurs with alone hearing, smelling or thinking about the dentist or before related stimuli such as washing your teeth, fus or on the lips ...), fears are also widespread to hospitals and injections so the attitude against it will be decisive when it comes to establishing or not the specific or general phobia preventing themselves on many occasions that take controls preventive and even the administration of treatments to certain diseases that would take them in time would not cover any problem.
Other types of frequent fears
In addition to the views there are many more stimuli that can be triggers of fears and that can later derive in phobias.
Among the most frequent we find:
- Fears derived from natural environments As are fears of storms (thunder and lightning), to the wind, to the water, to the intense noises, to the mountains, to the sea ..
- Fears derived from specific situations As public transport, bridges, heights, tunnels, elevators, flying by plane or boat travel, cars (driving or traveling) closed or open spaces ..
- Other types can refer to situations that can cause choking, vomiting, diarrhea, incontinence, to contract diseases, to fall if we are not close to walls or nearby media, to suffer from vertigo, to speak in public, to suffer accidents, to be injured, to be trapped In a jam or in small places, to physical sensations, to lose control, to faint, to go crazy, to have to defecate or urinate outside the home ..
It has been proven that in general have a phobia of the type that is increases the possibility of having fears (not necessarily phobic) of one or more of the other fears. In addition Not all phobias share the same clinical characteristics The differences will depend on the age, the beginning of the problem, on the sex, the pattern of physiological, cognitive or motor response, on the subjective and objective experience, on the situation, on the family history, on interference in the daily routine , of the time dedicated to planing what to do to avoid the phobic object, etc ..
The majority of phobias derive from basic specific fears are considered Hence the importance of preventing them and solving them before they become clinically significant fears because unresolved fears can lead to future phobias both in children and adults. Previously it was thought that phobic fears in childhood and adolescence could send without psychotherapeutic treatment but evidence shows that the general tendency does not seem to be this and in general We can say that the higher the number of specific phobias or specific fears accompanying these the lower the probability of recovery.
Specific phobias, also simple or focal called, They represent a minimum part of the phobic disorders seen in the clinic and this may be due to the fact that most patients do not seek help and when they do it is because they already present very high levels of pathology that incapacitates them considerably to develop a normal life , among the most frequent consultations we find:
Specific phobias
They are very common in both children and adults. In both cases they can be overcome without major difficulties with psychotherapeutic treatments. Phobic stimuli will be specific and specific situations or objects such as animals, darkness, water, heights, elevators, driving, traveling by plane or other means of transport, closed or open places, injections, eating specific foods, dentists, infection of diseases, defecation or urination in public places, firecrackers and tacas .. Specific phobias usually appear during childhood or adolescence, have a tendency to persist in adulthood and if they are not treated in time they can persist for decades. The degree of disability will depend on how easy the person is suffering from avoiding the phobic situation. People who suffer from this type of phobias are aware that their fear is irrational and disproportionate to real situations, comes triggered by the presence or anticipation of the phobic stimulus and They avoid it by all means at your fingertips. The exposure or anticipation of the phobic stimulus will immediately cause great anxiety, they even fear panic that they can experience and to the negative consequences that can derive from it so that their anticipation will be continuous as well as their avoidance, in case of not being able to Avoiding anxious manifestations will be so considerable that they are still going to convince themselves to a greater degree of the need to continue avoiding it, being continuously in a vicious circle that is impossible for them to leave.
Social phobias
Like the other phobias the Social phobia is characterized by extreme fear, exaggerated, disproportionate and loaded with great anxiety in social situations that for most people will not represent any danger Real but that, however, for those who suffer from it, they will make it impossible for them to react normally to situations in those can be observed by others, they have to speak or act in public, to relate to unknown people, perceive that they can be evaluated or analyzed from any manner,… They are hypersensitive people to criticism, With low self -esteem, with deficits in assertiveness and social skills, with exaggerated fear of feeling rejected, humiliated or criticized, they themselves are exaggeratedly autocritical, so they will avoid all those social situations or public performances that can put them in evidence in a way or other. They will frequently develop generalized anxiety disorders and depression and can even reach addictions as an attempt to solve their social deficits.
It seems that the social phobia is suffered by equal men and women, generally It usually appears in adolescence with a history of shyness during childhood. It may appear as a consequence of an experience experienced as stressful or humiliating or slowly due to a continuum of situations in which the person due to their social inability experiences them with a great load of anxiety. Evolution is usually chronic with a tendency to get worse and persist throughout life If it is not effectively treated by psychotherapy. Generally those affected do not usually seek help, perhaps because they consider that it is something immodifiable and inherent in their character and when they do it is for serious personal, labor or social reasons that prevent them from carrying out activities necessary for normal daily performance.

Agoraphobia
Being the phobia that presents greater disability Since you can imprison people in their own homes, it is perhaps one of the most frequently seen disorders in consultation, especially women. It is a pathology in which More and more situations are avoiding more and more Until a time getting when they can't even get out of their own houses. The anxiety they experience just thinking that they can be trapped somewhere or situation where they cannot escape or find help, in case of an anxiety or panic attack, it is so great that it leads them to take all kinds of measures and precautions That makes it impossible to be in agglomerations, queue, travel in means of transport, go to theaters, supermarkets, restaurants ... for them any place can represent a problem so they are generalizing to multiple situations and stimuli, due to the association that leaves producing between the internal sensations perceived as highly alarming and the evaluation of both real and imaginary that is done in this regard, in such a way that every time they are the broader and most avoided anxious situations, which in turn in turn strengthens more and more the problem,reaching extremes that neither alone nor accompanied can risked out given the immense generalization that occurs. Its anticipations are extreme and the disorders that originate very severe Hence, it is essential to go to a qualified professional to help them solve such a highly disabling problem.
Both fears and phobias and consequent Acquisition of enough resources and skills, that the consequences are not as terrible as they thought and that at all happened to what they feared so much.
Therapies
There are different techniques to effectively face these disorders, techniques that will be similar for both children and adults although with small differences in the way of applying them, depending on the age or the characteristics of the problem, so it will be important to perform a good analysis functional to provide enough information of what is really happening in each case to, depending on this, to act in the best possible way.
Among the most used techniques and that best results are providing when fighting these problems we can contemplate the following:
Psychoeducation: fundamental for the person to understand what is really happening, both at the cognitive, physiological and engine level, what is maintaining the problem and why, what can you do to control the three levels of response ... It is about contributing The maximum relevant information related to both the phobic stimulus and with the maintenance of the problem using informative psychotherapies, literature ..., but above all an understandable language of the different concepts related to both the acquisition and with the maintenance of the problem.
Systematic desensitization: especially indicated to learn to respond without anxiety to stimuli that cause inappropriate responses. Its objective is, to face the threatening situations gradually (both in imagination and in reality) using a hierarchy of previously established situations, associating all this with progressive relaxation and with pulmonary breathing and slow diaphragmatic until counteracting some emotions with other and get a habituation to threatening situations. It can be used in both children and adults because it allows us.
Techniques to handle anxiety that accompanies phobic disorders:(Progressive muscle relaxation, slow diaphragmatic breathing, distraction, self -instructs, focus of attention ...) There are numerous relaxation techniques but among them highlights the "progressive muscle relaxation of Jacobson" both for its simplicity of application and for its high effectiveness in the treatment of the anxiety. The fundamental characteristic is that it allows to generate, through the absence of tension, answers incompatible with the stressful activation of an organism. It clearly allows discriminating signs of voltage in the different body muscles by learning systematic tension-relaxation exercises. The relaxation that is obtained at the muscle level automatically generates the relaxation of both the autonomic nervous system and the central nervous system, which in turn enhances both cognitive and emotional relaxation allowing to execute without difficulty behaviors that interfere with those of flight, escape or avoidance, considerably increasing success in future clashes.
Exposure therapy both live and through images: causing behavioral experiments that allow to progressively desensitize the phobic element and gradually eliminating all the answers aimed to avoid the feared situation both at the cognitive and physiological and motor level. In the exhibition we will use the exhibitions combined with relaxation techniques, self -instructions ... to progressively generate habituation, satiety and desensitization through both live and images to phobic stimuli. Its fundamental objective will be to cause emotional states incompatible with anxiety and phobic reaction. The duration and intervals of the exhibition will be adapted based on the answers that are achieved, increasing both as the clashes are overcome.
Modeling techniques: Very useful to solve phobias when used for therapeutic purposes because they allow, by observing, learning from the adaptive behaviors made by other people to be able to modify their own. They can be used with both children and adults, but it is children who can benefit the most. The observation of models can be done through drawings, films, real cases ... The child observes another child how he faces the feared situation, how he approaches, how he does it without anxiety and even how he enjoys the model ... A From there he is encouraged to carry out the behavior through relaxation, exposure and confrontation of the feared situation, supporting him, encouraging him and motivating him at all times until little by little his fear will be overcome.
Emotional staging techniques: Like the previous one very indicated for children because it combines relaxation, systematic desensitization, the participant model, emotional images to inhibit anxiety (images that can draw or create themselves) the role game with papers exchange, and something very important the positive reinforcement before any approach and confrontation behavior to the feared object.
Cognitive-behavioral therapies: are the therapies that are best giving.Cognitive-behavioral therapies combine cognitive restructuring procedures, relaxation-desensitization, training in resources and skills to be able to expose and face phobic stimuli, problem solving, self-instructions, thought control ... The foundation of these therapies consists of encouraging People who suffer from these disorders to continuously confront their catastrophist and highly negative beliefs with reality eliminating from their repertoires the avoidance and increasing the exhibitions until a desensitization that allows them to face and adapt to situations in a much more realistic, adaptive and rational way in such a way that they can be able to clearly discriminate what is really dangerous and what is the product of their imagination but does not represent any real danger.
Therapies based on virtual reality: Very useful to make exhibitions as many times as we want without having the phobic stimulus in front of therapy because all the therapy is performed at the virtual level.

recommendations
Fear appears. ¿What not to do?
- Laugh at the reactions presented by the child.
- Allow others to laugh at him.
- Compare him with other children who do not present their fears.
- Criticize or punish you for being afraid.
- Make public reactions and behaviors to fear.
- Insist with arguments and reasoning continuously remembering your fear.
- Force abrupt or authoritarian ways to face phobic stimuli.
- Threaten to the stimulus to the one you are afraid ("if you do not eat the bad man will come," if you do not do this or that I will lock you in the dark room "...).
- Protect him in excess avoiding any threatening stimulus or any confrontation to the phobic stimulus ..
Fear appears. ¿TO DO?
- Act with maximum peace of mind when you present the fear response, or the "panic attack".
- Talk to low tones, paused rhythms and movements and as relaxed as possible.
- Give affective support and, whenever possible, physical contact.
- Train the correct confrontation reactions and encourage you to play to check your progress.
- Let him face the little fears, that he gets used to them alone. Eg. Waves of the sea, darkness, animals, noises ..
- Congratulate him for any progress in overcoming his fears, avoiding "coletillas" of the type: "It was already time that" total was not so much "..."
- Convince him that you don't have to be ashamed for feeling fear of certain things. Use phrases like "I was also afraid of ..." "You are much braver than me"
- Offer correct models of how to act. Eg.: Mount the swing, enter the dark ..
- Go approaching the stimulus of fear progressively, little by little and always in a pleasant and fun environment for the child
Attitudes that can prevent the appearance of phobias
- It is important to test and contrast to what extent what one fears can have the consequences that one believes. The key for fears to appear is in the immediate well -being we get when we escape and avoid what we fear so much. By avoiding it, we prevents learning to control it.
- From education It is very important to teach a child to check if something should be or should not be feared: Pool, dogs, darkness, be or sleep alone ... will make you later, in adulthood it is much easier to face other fears: death, heights, talk to others ..
- Make the child check Through experience and graduated, What happens when you stay in the room in the dark, or what happens if you play the bottom of the pool, or what happens if you play a puppy ... for example, it will help you perceive that what surrounds you should not be feared in excess. On the other hand, parents' fears, the search for guarantees that nothing will happen to the child, when they are exaggerated too much, not only will it greatly difficult to reduce fears in the future but will expand them.
- Sometimes we are the parents themselves who transmit fears to our children by taking too many precautions derived from our own fears.
- It must also be specified that not everything that is feared must be overcome, After all, the feeling of fear, initially, is the adaptive response that our mind gives to favor the probability of survival.
- In other words, fears are necessary because they are often totally adaptive. The problem is when they cancel us and block us without being able to move forward or when we are incapacitated to lead a normal life, just then have to act.
- Use a positive education style, using educational techniques based on kindness, calm and respect for children, rather than using punishment and threat. Above all, physical punishment or psychological threat should not be used, there are other much more effective ways to educate.
- Avoid scaring the child even if it is "joking", Especially the scares are contraindicated in the dark.
- Be attentive to what the child sees on television: You should not see fear or violence films that lead them to exaggerate in their imagination fictitious and unreal situations but that they assume them as real.
- When the child cries at night because he is afraid it is preferable to calm him in the dark And then, if perhaps, turn on the light, so that you never associate darkness with fear.
- Teach him to solve the small difficulties of daily life by himself. Do not give it the things done or avoid the small frustrations with which you have to face.
- Teach him to observe, see and reinforce any behavior of courage and confrontation that has as small or minimum that it may initially seem.
- Do not use fear to control you: "If not, the coconut will come, the witch, the man of the bag ... "
- Do not tell you stories or horror stories, nor stand out especially or exaggerate the most frightening aspects of traditional stories, Always provide solutions and alternatives to solve problems.
- Read or make read stories in which children like him overcome small fears or difficult situations, Mount funny cartoons about those situations that can be scary and that he provides alternative solutions and narre cartoons.
- If we are afraid of something we must learn to solve it, to maintain control And to also try to overcome our own fears so as not to transmit them to them, and thus be able to serve as models of action in the face of our children's fears.
10 rules to face panic
- Start by accepting fears. Accepting fears and concerns is the first step to get rid of them. We should not feel shame or guilt for being afraid. If they are assumed and accepted we will be able to speak and rationalize it. The mere fact of telling things automatically lose importance.
- Remember that sensations are nothing more than an exaggeration of normal body reactions to a perceived danger. They are not harmful or dangerous - only unpleasant. And above all nothing worse can happen because in every process anxious everything that goes up.
- Wait and give time for fear little by little to decrease. Do not flee from it, simply accept it until we control the anxiety it generates but facing him. Observe something fundamental and that is that, As soon as we stop adding distressing thoughts Fear will begin to fade by itself.
- Change the negative thoughts that usually accompany these states for positive thoughts. Do not add anxious thoughts to what is happening or about what can happen to us. It's very important Learn to stop thinking When we detect that we are giving ourselves negative self -instructs ("I will not be able", "this situation is horrible" "I can't" "I'm very afraid" ...). At that time shout inwardly "¡HIGH¡”, And replace these messages for: Positive thoughts ("I'm going to get it", "the situation is difficult, but I can with her" "I'm afraid but I will stop having it" "I'm going to face" "I'm going to try, sure I can" ...)
- Observe what is really happening in the body right now, at this time, FAIRWhen the problem is beginning to occur In order to control the responses in the most relaxed possible way without making strange or catastrophic anticipations loaded with bad omens. It is also very important that Instead of worrying, let's do something fun as for example., Think about something pleasant while I face, do something we like (take the bike, read a comic, play ...) will make worries forget. Exercising will also help us to be more relaxed and release the tension accumulated by fear.
- Wait and give time to fear so that little by little it decreases. Do not run away from him or avoid it, simply learn to accept it until little by little we control it. Observe something fundamental and that is that, As soon as we stop adding distressing thoughts Fear will begin to fade by itself.
- Learn resources and skills to face fear being the key exposure, confrontation and non -avoidance - without avoiding it or fleeing- but taking advantage of the situation as an opportunity to practice, learn, advance and fight it. It is very important to learn to breathe deeply. When we are nervous we breathe very quickly and superficially, because we only fill the upper part of the lungs. We can improve breathing, making it slow and deep. To do this we fill the lungs slowly to the bottom, taking the greatest amount of air through the nose, and then we also slowly expel it through the mouth. And while we exhale the air, we can think for eg. how when expelling the air we eliminate with him the fears and things that concern us.
- Use relaxation as an essential element to face phobic situations.You can't be afraid and be relaxed at the same time. If we learn to relax we can counteract the sensations of fear and help us approach or overcome the dreaded situation.A very easy method to relax the muscles is to concentrate on a part of the body (for example the arm) and tighten your hand hard for a few seconds to feel the tension of the arm muscles; As soon as you stop squeezing you will notice relief and the feeling of relaxation in the arm. You would have to repeat it once or twice and do the same with all parts of the body until they dominate the technique.
- Also use mental images to imagine pleasant scenes while visualizing how fears or concerns disappear. If we already know how to breathe slowly and relax the muscles, we can try to imagine a pleasant scene and provide us with peace of mind (eg., See you lying on a quiet beach, noticing the warmth of the sun's rays on our body, or we are traveling on a cloud, floating in the air, while the wind takes our fears ...)
- Always think about the progress we have achieved despite the difficulties. This will reinforce us considerably and make us feel very proud of the achievements achieved, in addition to providing us with increasing security.
- Help us with self -registros writing the fears we are facing, the strategies used to overcome them, or simply write what we say or we must tell ourselves as soon as we feel fear or concerns. It will help us to better understand what happens to us, what can we do and how we can face when overcoming fears. This technique provides many self -control strategies at all levels and can help us a lot to solve multiple problems.
- As soon as we feel a little better, let's look around and plan the next step to continue moving forward. We generally avoid thinking about our fears, because we feel more secure and we believe that in this way we will find us better. ¿But, and if we did the opposite? We can try to see what happens and plan the following steps to continue moving forward and welcoming. We discover that these fears no longer scare us as much as we believed, or it is simply possible that we manage to see the situation in a very different way as we thought.
- When we are prepared to continue, let's start again in a quiet and relaxed way. There is no need to run, let's do it little by little, step by step, progress but without stop.

Final reflection
It is always better to prevent cure: sometimes we can prevent situations that cause us fear. For example, a child who is afraid of nightmares, should not see before bedtime films that can scare him, nor should he have copious or very strong and indigestible foods that can cause discomfort that could give rise to conditioned fears or drink drinks with caffeine or any other exciting substance. ¿Why cause a situation without first being prepared to solve it?
¡And something very important!
Given fears, therefore, with avoidance, fear will grow, will extend and generalize to many other situations, so although it generates some anxiety, it is much better to expose, face, solve it and analyze the consequences that avoid it. The anxiety that may generate when trying to solve it will always be much less than the problems generated by its maintenance.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Fears, anxiety and phobias: differences, normality or pathology?, We recommend that you enter our category of emotional and behavioral disorders.

