The changes that occur in the brain after being a mother

- 3377
- 17
- Miss Drew Stroman
"It was a great shock. I had no idea what maternal instinct was. I had no idea that I was going to have such a tremendously strong instinct, I had no indication of it before my children were born, but it was something that emerged from the depths ... " Leonora Carrington
We have all heard that having a child changes our lives, which since we hold our children for the first time, we know that nothing will be the same again. Although these statements may sound to Cliché, there is nothing further from reality: Conceiving a new life literally causes changes in the brain of mothers that influence their way of feeling and behaving.
Content
Toggle- Everything changes and also our brain
- Hormonal changes
- The amygdala and emotional responses
- Becoming a mother is also falling in love
Everything changes and also our brain
From feeling intense emotions when seeing the baby's smile until he jumps to protect him as soon as his crying sounds, the behavior of the mothers has been observed for centuries. However, it has not been until recently when these behavioral changes have begun to relate to the changes that happen in the brain.
Specifically, a study carried out by the Autonomous University of Barcelona demonstrated through magnetic resonance images a gray matter reduction in certain areas of the cerebral cortex of pregnant women, a change that was maintained during the two years after childbirth.
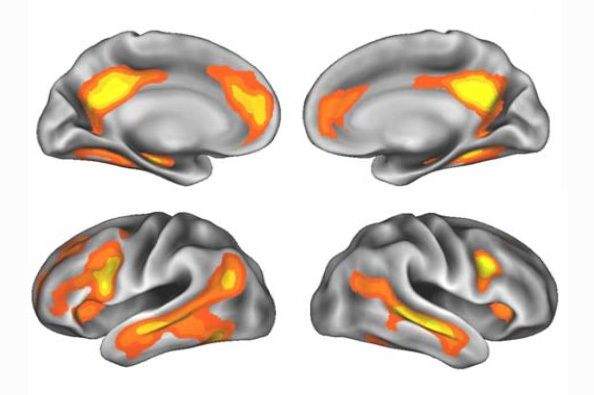
This reduction It is not at all a cognitive deficit, As Susana explains Carmona, Co -author of the study, but a total targeting in everything that refers to the baby: a selection of neuronal connections that prevents the communicative distraction of neurons, favoring greater maturity in mental processes.
Hormonal changes
There is one greater concentration of gray matter, as well as an increase in the activity of the regions that control empathy, anxiety and social interaction; specifically in the prefrontal cortex, parietal lobes or the midbrain. These are driven by an avalanche of hormones that begins during pregnancy and helps attract the mother to her baby during the postpartum period.
This increase huge hormones such as progesterone or estrogen During pregnancy, it only occurs in such similar amounts during the adolescent stage, causing drastic changes in the brain. The feelings that cause these changes can become so overwhelming that for some scientists they could be key to understanding the anxiety and depression that some mothers may experience after childbirth.
"It is what we call a common aspect in almost all obsessive-compulsive behaviors that occur during the first months, after the arrival of the baby," explains the neuroscientific researcher Pillyoung Kim, when talking about mothers who refer constant thinking patterns of thought repetitive and checking about aspects related to babies.
 Brain that travels = healthy and happy brain
Brain that travels = healthy and happy brain The amygdala and emotional responses
An area of great interest among scientists is the tonsil, a subcortical structure that is in the temporal lobe. This structure helps in the emotional memory process and is highly involved in Emotional reactions Like fear, anxiety or aggression.
During the following weeks after childbirth, The activity of the amygdala grows In normal brains and this growth seems to be related to Hypersensitive behaviors From the mother to the baby: Reward circuits, The same ones that are activated when we feel other types of pleasures, are launched in the mother with the simple fact of looking at the baby, as they demonstrate different academic studies.
Becoming a mother is also falling in love
According to the neuroscientific researcher Ruth Feldman, “Maternal oxytocin levels (also called love hormone), increase greatly during pregnancy and in the postpartum period. The mother is wrapped in the child's care, the greater the increase in oxytocin ".
According to Feldman, becoming a mother makes Our brain is very similar to the brain in love; This would help explain the feelings that first -time parents describe when taking their newborns in arms.
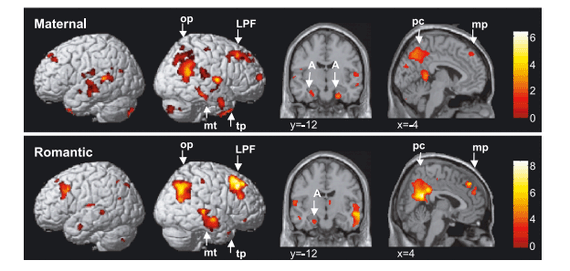
The amygdala, as we explained above, becomes more active, as well as reinforcing networks: "In our research, we show how similar changes occur both in the brain of lovers, and in that of first -time mothers"
It seems that greater changes occur when you have The first child, While it is not yet clear if the mother's brain once is once again the same as she was before being a mother.

