Temporal lobe function, areas, characteristics and injuries

- 3366
- 186
- John Von
The temporal lobe is a part of the brain responsible for many functions related to hearing and language. It also performs important visual tasks, in addition to regulating emotions. ¿You want to know every detail of the temporal lobe? Such as, for example, what controls the left temporal lobe or what are the functions of the right temporal lobe. In this psychology-online article, we will talk about the functions, areas and characteristics of the temporal lobe and also on the lesions That can occur.
You may also be interested: parietal lobe: function, parts, characteristics and index injuries- What is the temporal lobe
- Temporary lobe function
- Temporary lobe areas
- Temporary lobe injuries
- Temporary lobe seizures
- Temporal lobe epilepsy
What is the temporal lobe
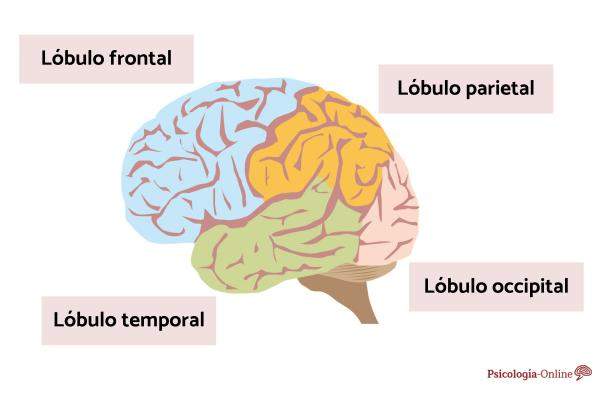
The lobes are in the right and left hemispheres of the brain. So, each side of our brain has four lobes, they are: frontal lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe and occipital lobe.
The temporal lobe is the second largest structure in the brain, The first is the frontal lobe. It occupies approximately a quarter of the cerebral cortex.
Another characteristics of the most important temporal lobe is that it establishes connections with the limbic system. But, ¿What is the limbic system? It is a system that is responsible for social emotions and behaviors, is directly related to the affective nature of sensory perceptions.
Temporary lobe function
The temporal lobe is located on the sides of the head, behind the front. ¿What is the function of the temporal lobe? Their fundamental skills are:
- Memory
- Recognition
- Affectivity
The temporal lobes are the regions of the brain responsible for receiving and regulating sensitive stimuli, language, memory, smell information.
They are also responsible for the ability that people have to recognize objects and faces, emotions, attention, part of learning, affection, reading and writing.
The temporal lobe is located in a region where the primary cortex of the brain audition is also found. Therefore, he is able to handle auditory language and speech understanding systems.
Temporary lobe areas
The temporal lobe is one of the parts of the brain and is divided into different areas. Next, we will see what are the areas of the temporal lobe and what does each part of the temporal lobe control:
Auditory cortex
- Works in the audition process
- Perceive sounds
- Perform coding, decoding and interpretation of auditory information
Medial temporal
- Participate in memory and recognition
- Processes information and helps to move from short -term memory for the long -term
- The left hemisphere is responsible for verbal information
- The right hemisphere stores visual patterns
Association Area:
- Intervenes in perceptions, in memory and feelings
- Participate in memory and learning
- Regulation of sexual behavior
- Emotional stability maintenance
Supramarginal turn
- Participate in the tactile recognition
- Participate in language
- Ability to make the individual recognize the relief of letters through the fingers and associate them with sounds
Angular turn
- Allows the association of visual information with the auditory
- It allows to produce a change in the type of data with which the brain works
Wernicke area
- Language processing and understanding
- Allows verbal communication between individuals
In the following article, you will find more information about the Wernicke area, its location and functions.
Temporary groove cortex
- Works in auditory and visual information
Temporary lobe injuries
The lesions that can occur in the temporal lobe and that produce a series of symptoms related to their functions are:
- ACV
- Tumors
- Craniocerephic trauma
- Damage to the cerebral cortex that affect the temporal lobe
- Specific neurological disorders
¿What happens if the temporal lobe is damaged? The consequences of these injuries are the following:
- Deafness
- Hearing problems
- Auditory hallucinations
- Memory loss
- Personality changes
- Motor Apraxia
- Sensory stimuli response deficit
- Wernicke aphasia
- Learning alterations
- Reading affectation: in people with lesions in the angular turn, reading is usually affected, being very slow or non -existent.
Temporary lobe seizures
We can cite the seizures of the temporal lobe, also named Focal seizures with consciousness alteration. It is called that because some people are still aware of what happens, although during more intense seizures, they may seem aware, but they are not.
Temporary lobes process emotions and are important for short -term memory, so some symptoms of temporary lobe seizure can be related to these functions.
The causes of these seizures are still unknown, but studies indicate that they can be for a anatomical defect or a scar on the temporal lobe.
These temporary lobe seizures are treated with medication. And, for individuals who do not respond to medication, surgery can be an alternative.
Temporal lobe epilepsy
We can also mention the epilepsy of the temporal lobe that usually begins around 10 years of age until adolescence, but you can develop at any age as long as there is a lStructural is in the temporal lobe.
In the epilepsy of the temporal lobe, focal crises occur:
- If the individual remains aware during the crisis, then it is named after Conscious focal crisis.
- In the same way, if the individual loses consciousness during the crisis, it is called Focal crisis with alteration of consciousness. These crises are described as a special sensation or experience, includes sensations of having previously lived the current situation, a smell, taste, sound or vision, an emotion, nausea or sensation of elevation in the abdomen. The individual who presents an alteration of consciousness in the crisis can stare or rubbing his hands.
Temporary lobe epilepsy can be caused by Infections, lesions and brain tumors, Good as genetic factors or changes in brain structure. It can be diagnosed with a blood analysis, an electroencephalogram or image diagnostic techniques.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Temporary lobe: function, areas, characteristics and injuries, We recommend that you enter our category of neuropsychology.

