Pheromones and their impact on our behavior

- 3541
- 1108
- Herbert Ritchie
Feromones are chemical substances produced by organisms that can influence the behavior of other individuals of the same species. In humans, it is believed that pheromones can affect sexual attraction and couple selection, as well as the regulation of the menstrual cycle of women and the synchronization of circadian rhythms.
Although research on human pheromones is still limited and controversial, there is evidence that Certain pheromones can influence the sexual attraction and perception of the attractiveness of others. For example, it has been shown that women can detect the presence of male pheromones and that this can affect their couple choice. In addition, it has been found that women who take oral contraceptives have a lower sensitivity to male pheromones, suggesting that sex hormones can affect the response to pheromones.
Content
Toggle- Psychological stimulation of pheromones
- Studies on the impact of pheromones on people
- Relationship of pheromones with the female menstrual cycle
- The impact of male pheromones on the female menstrual cycle
- How pheromones are detected and transmitted
- Neurological activation of pheromones
- Pheromones and their effects of mood
- Genetic compatibility and pheromones
- Conclusion
- References
Psychological stimulation of pheromones
Psychological stimulation of pheromones refers to the ability of certain psychological stimuli to increase pheromones production in the human body. It has been shown that psychological stimulation can have a significant effect on the production of pheromones in some cases.
For example, it has been found that Exposure to certain odors can increase pheromones production in the human body. It has also been shown that psychological stimulation, such as sexual excitement, can increase the production of pheromones in men and women.
Most studies have shown that Human sweat increases physiological activation, in one way or another. The idea that something about we are not even aware affects such a primary level to our behavior is, at least, disturbing for some people, but in reality pheromones are controlled by the combination of all our senses.
It is important to realize that any smell can affect our behavior, but pheromones are produced by our congeners (members of the same species) and play a key role in communication. Studies show that pheromones are processed differently than common odors.
Studies on the impact of pheromones on people
In a study by Bensafi et al (2003), the electrocardiogram were analyzed, The pulsations, blood pressure, abdominal and thoracic respiration of a group of subjects of both sexes after smelling androgens and estrogens. Most showed significant changes in temperature and skin conductance. The increase in excite.
In other pheromones studies it has been found that there is an increase in physiological activation and skin conductance in addition to a decrease in skin temperature due to its effect.
It seems that pheromones (male or female) applied topically increase sexual attractiveness. And in another study it has been observed that the men who used pheromones had greater sexual activity with their sentimental partners, although not an increase in autoerotic behaviors.
In another study, Jacob et al. (2001) rehearsed with androgens and estrogens by diluting them with other chemicals to hide their smell. They concluded that androgens can influence positively in the mood and increase excitation in both sexes. But Jacob suggested that the effects of these compounds are dependent on the context, since the results vary quite according to different studies.

Wyart et al (2007) In his pheromones study, cortisol hormone levels in women increased. Cortisol is generally released when a person suffers from stress, which suggests that it can be an inducer of increasing excitation. Cortisol can also affect levels of serotonin in the brain, What would have an effect on mood. In this study there was an increase in sexual excitement, physiological excitement and a better mood in the women involved.
Relationship of pheromones with the female menstrual cycle
It has been suggested that pheromones can have an impact on the female menstrual cycle, including the synchronization of the menstrual cycle between women who live together or spend a lot of time together. This is because pheromones can transmit social and biological information among individuals of the same species.
In laboratory studies, it has been shown that exposure to women's feromones can affect the beginning and duration of the menstrual cycle of other women. In addition, it has been found that women can detect pheromones from other women and that this can affect sexual attraction and couple choice.
The menstrual cycle of the woman exposed to the axillary secretions of other women is shortened or extended depending on the phase of the other women's cycle. For example, during the late follicular phase, the cycle is shortened by a delay in liberation luteinizing hormone (LH), necessary for ovulation. During the ovulation phase of the cycle it accelerates in the opposite manner. The final result is that some of the female pheromones affect each other so that over time. This synchronization is sometimes known as the McClintock effect.
The impact of male pheromones on the female menstrual cycle
curiously, Male pheromones are also able to affect the female menstrual cycle, accelerating and increasing fertility in women. Cutler and Preti, 1986, showed in their investigation the importance of the presence of male pheromones in women's biology. They found that Regular sex decreases fertility problems in women, regulates menstrual cycles and correlates with softer menopause.
The cycles of women exposed to male sweat on their upper lip for a month, short. Exposure to androgens (a pheromone produced by men) accelerates the appearance of the peak of the LH necessary for ovulation, by affecting the hypothalamus to secrete the gonadotropin liberating hormone (GNRH). The researchers also observed an increase in the general relaxation of women.
It has also been found that exposure to male pheromones during the fertile phase of the menstrual cycle, can not only increase pheromones production in women, but also affect the selection of a couple.
However, it is important to take into account that the research on pheromones and the female menstrual cycle remains limited and that more studies are needed to completely understand the underlying mechanisms and the scope of the influence of pheromones in the regulation of the menstrual cycle.
 Is correct sexual education today?
Is correct sexual education today? How pheromones are detected and transmitted
Pheromones are detected by Nose olfactory receptors. These olfactory receptors are specialized in detecting specific chemicals, including pheromones. Once the pheromones are detected by the olfactory receptors, signals are transmitted to the brain and are processed in specific areas of the olfactory system. Olfative information is integrated with other sensory and cognitive signals to produce a behavioral response.
The pheromones They can also be transmitted between individuals through direct chemical communication. For example, mammals can produce pheromones in the specialized glands, such as mammary glands or skin glands, which are then released in the environment. Individuals can detect these pheromones through smell and respond to them behaviorally.
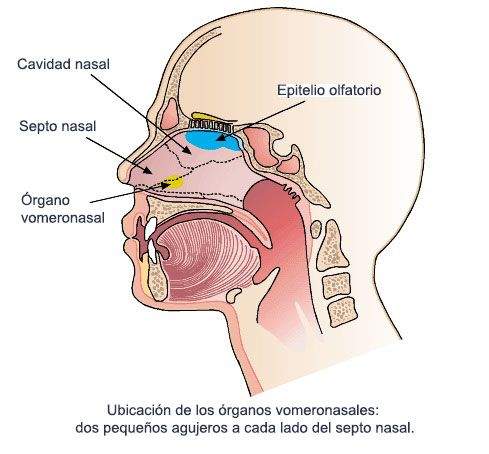
In humans, pheromones can also be transmitted through sweating and other bodily secretions, such as saliva and tears. However, research on human pheromones remains limited and controversial, and more research is needed to completely understand the mechanisms for the detection and transmission of feromones in humans.
Neurological activation of pheromones
The neurological activation of pheromones refers to the response of the nervous system to the chemical signals that occur when pheromones are detected. When pheromones are detected, chemical signals are processed by the nervous system and transmitted to specific areas of the brain that are involved in the perception and processing of olfactory stimuli.
In humans, it is believed that Feromones can activate specific areas of the brain, such as the orbitofrontal cortex, which are involved in the perception of emotions and decision making. In addition, it has been found that pheromones can activate the limbic system, which is involved in the regulation of emotions and in the formation of memory.
It has been shown that the neurological activation of pheromones can affect behavior and perception in humans.
We have already seen that exposure to male pheromones can increase the sexual attraction of women towards men. It has also been shown that Exposure to mothers feromones can affect the behavior and development of newborns.
Functional image studies of the brain can show exactly how the brain is activated when a person is processing pheromones.
The hypothalamus controls behaviors such as fighting, flight, food and reproduction. The hypothalamus contains various regions with sexual dimorphism, which differ in size between men and women. For example, The female smell activates certain cores of the hypothalamus in men. Hypothalamus activation is common in the face of ordinary odors, but the difference in activation between men and women is consistent with theories about sexual dimorphism in the brain.

Studies reveal that these differentiated areas are related to sex and sexual behavior. For example, The preoptic nucleus is twice in men than in women, So it is thought that you can participate in sexual behaviors, mainly masculine. The ventromedial nucleus intervenes in defensive behavior, and also seems to participate in female sexual behavior. More generally, the previous hypothalamus has to do with thermoregulation and sweating, what we have seen are the direct effects of pheromones.
Zhou and Chen (2008) conducted a study using axillary sweat to explore differences in brain activation. They exposed women to male sweat collected during sexual excitement and found that the physiological activation of women was significantly higher when exposed to "sexual sweat" compared to non -sexual sweat. The hypothalamus responded more actively to sexual sweat than neutral sweat.
Pheromones and their effects of mood
Although the research on pheromones and mood in humans remains limited, it has been shown that certain pheromones can have effects on emotional perception and mood regulation.
Apparently The mood can be communicated through chemical substances found in axillary sweat. The sweat collected from men and women, either while a fun video (happiness) or terrifying (fear) is visualized can be recognized later. In an experiment conducted by Chen in 2000, sweat was collected from women identified as "happy" and women identified as "scared". Subsequently the men who worked in the study were able to distinguish both types of sweats quite effectively.
In a more recent study by Marazziti et al (2010) they found a direct correlation between axillary compounds and serotonin, Mood affects. The male sweat modulates the affinity of the serotonin transporter, which means serotonin stays longer on the receiver and has a longer effect with an increase in the effectiveness of serotonin. They also observed an increase in impulsivity in women against men with high levels of serotonin, showing a positive correlation between serotonin values and romantic relationships.
 Otelo syndrome, pathological jealousy taken to the extreme
Otelo syndrome, pathological jealousy taken to the extreme Genetic compatibility and pheromones
As we have already seen a person tends to feel greater attraction towards another person depending on certain odors.
A time ago a study was published by the University of Bern (1995) in which some of the genetic reasons that hindered incest. According to the results found, they have to do with the variety of alleles in the genes. According to this study, Different alleles attract and the like repels, habitually. The idea is that a person feels greater attraction for the smell of someone who has alleles other than their own. According to this theory, this would be a protection that would have been generated through natural selection to provide greater genetic diversity to the couple (and the population).
So, Our body generates a more receptive response when immune systems harmonize and fit each other. This factor has recently been exploited by an offline offline agency in the United States. The service acknowledges based on the conclusions of this research on which different women sweated for several men were smelled. The result was that each woman was attracted to the smell of who had the immune system more different from her. The explanation, according to the study, was that they "genetically complete" their immune capacity to give it to their future children. And apparently detecting these genes "it is something that the body does unconsciously".
Conclusion
Reproduction is the most important aspect in the survival of a species. For this reason it makes sense that they exist mechanisms outside our control that urge us not only to procreate, but to find colleagues who will give rise to the most successful offspring. Feromones are just another way for which we can communicate, both animals and human beings.
What happens in our brain during orgasm?
References
- Berglund, h., Lindstrom, p., And Savic, I. (2006). The response of the brain to pheromones in lesbian women. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103 (21), 8.269-8.274.
- Cutler WB, GE (2002). Pheromones, sexual attractiveness and quality of life in menopausal women. CLIMATERIO, 5 (2), 112-121.
- Jacob, s., And McClintock, M. (2000). Effects of the state of humor and psychological steroid signs in women in men. Hormonal behavior, 37 (1), 57-78.
- Touhara, k., and Vosshall, LB (2009). When perceiving smells and pheromones with chemosensory receptors. Annual Review of Physiology, (71), 307-332.
- « Screen apnea when screens affect our breathing and well -being
- What happens in our brain during orgasm? »

