The currents of psychology and its characteristics
- 5014
- 739
- Charles Fay
¿You wonder what psychological current is better? ¿You know all the currents of psychology? In this psychology-online article, we will see some of The main currents of psychology and its characteristics and the differences between contemporary psychological currents.
On the other hand, we will also discover the protagonists of psychological thinking, thanks to which psychology has developed, based on humanistic foundations, until an independent field of scientific research and application.
Let's analyze the main schools and currents of current psychology.
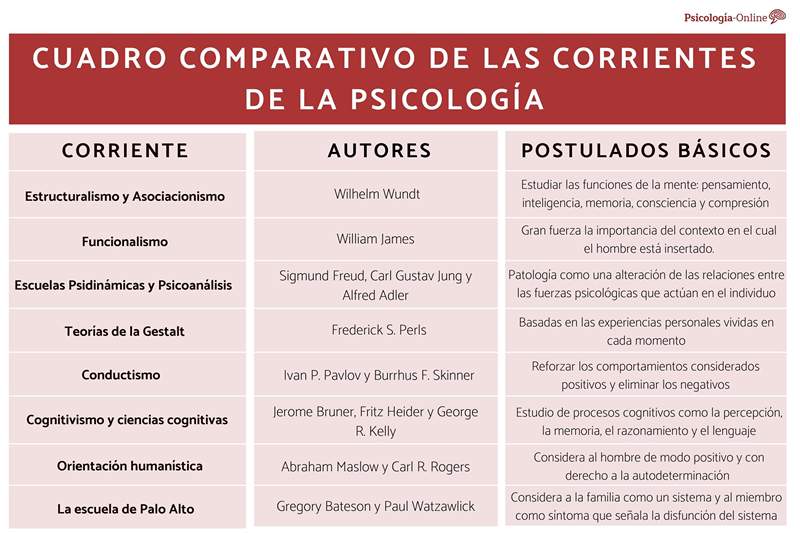
You may also be interested: what is functionalism in psychology: characteristics, theory and authors index- Structuralism and associationism
- Functionalism
- Psychodynamic and psychoanalysis schools
- Gestalt theories
- Behaviorism
- Cognitivism and cognitive sciences
- Humanistic orientation
- The Palo Alto School
Structuralism and associationism
When the first psychologists decided to study the strategies and modalities of psychic functioning, they focused their attention on the unique functions of the mind: thought, intelligence, memory, consciousness, understanding, etc. Even the most complex characteristics were decomposed and reconduated to these primitive factors. This functioning model took the name of structuralism, to indicate the basic functions of the psyche and its integration with the physiological structures of the nervous system. In this article we explain what structuralism in psychology is.
In the times of structuralism, it was not yet available for complex scientific instruments, and for this reason, the analysis technique placed by associationism was of a simple nature and resulted in the observation of the responses produced by the subject examined - concept of systematic introspection. The discovery of this observation methodology dates back to Wilhelm Wundt, Founder in 1879 of the First Experimental Psychology Laboratory in Leipzig (Germany). Wundt was also the first researcher to define himself with the term psychologist, so Wilhelm Wund is considered the father of psychology.
Functionalism
What happened in Europe with the opening of the first psychology laboratory, found a parallel event in the United States, where it will be born, thanks to William James, A study current called functionalism. This term was chosen to indicate the relationship with the representative functions of psychic processes, which for James are in continuous evolution and must be considered as the natural reflection of human adaptation to their environment. The theoretical opposition to the current of structuralist thought is evident, in which the psyche had to decompose in each of its functions. In the functionalist position, the Importance of the context in which man is inserted, to the point that mental processes are seen according to continuous and organizational development. In this article you will find more information about what functionalism in psychology is.
Psychodynamic and psychoanalysis schools
One of the contemporary psychological currents that has had the most strength is psychoanalysis and psychodynamic schools, which study the mental processes of the individual. Consider pathology as an alteration of relations between the various psychological forces that act in the individual, who nevertheless are each other in a relationship never static, but, precisely, dynamic. Sigmund Freud is the founder of psychoanalysis, and although before him there was already knowledge about dynamic processes, he first built a complete theory that allows us to explain both normal functioning and mental pathology. Thus different models are recognized during the development of your research: the first is the one based on the study of the unconscious, while the second takes the name of "structural" model (this, I, superego).
Psychodynamic schools have been characterized both by theoretical vivacity and the clashes between theories and people that have given rise to different schools. Since the first years of the twentieth century they have separated from the psychoanalysis of prominent authors such as Carl Gustav Jung and Alfred Adler, to acquire - since the 40s - the original contribution of many others that, on the one hand, have enriched the initial theory. On the other hand, they allowed a therapeutic approach to mental diseases such as psychosis, schizophrenia, autism, which were previously considered intractable. The psychology of the self is remembered, developed mainly in the United States, the English school, with the fundamental contribution of Melanie Klein to the study of children's psychic processes, and the studies of authors such as Anna Freud, Wilfred Bion and Donald Winnicott.
Gestalt theories
One of the most important modern psychological currents is Gestalt School. The psychology of the form, or psychology of the Gestalt, has elaborated with Frederick s. Perls A psychodynamic theory based on personal experiences lived at the time, in the "here and now". The needs, if they are not met, give rise to incomplete forms and psychological conflicts. Gestalt therapy tries to favor the termination of forms, for example, concentrating the significant elements of a situation to mobilize its energies in advantageous strategies. An example of this is the Gestalt proximity law.
Behaviorism
The clinical approach of behaviorists has always opposed that of psychoanalysis. For them the symptom is not the product of an intrapsychic conflict, but a problem in itself, and its elimination coincides with healing. Behavior therapies are derived directly from scientific discoveries, such as the classical conditioning and operating conditioning, respectively, due to Ivan P. Pavlov and Burrhus F. Skinner, have led to therapies that try reinforce the behaviors considered positive and eliminate negatives. Behavioral techniques are considered especially useful with those people who are too damaged to receive the help of psychotherapies based on verbal communication. In this article you will find more information about what behaviorism is in psychology.
Cognitivism and cognitive sciences
One of the main contemporary psychological currents is cognitivism. An orientation of experimental psychology, also called cognitive psychology, which privileges the study of cognitive processes as perception, memory, reasoning, language, etc. The individual acquires and transforms information from the environment and acquires the knowledge that influence their behavior through the cognitive processes mentioned. In particular, cognitivism revalue, as opposed to behaviorism, the method of introspection, but also uses heuristic knowledge and procedures in various fields of scientific research, such as cybernetics, information theory or neurophysiology. You can find more information about cognitivism in this article: cognitive theories: what are, types and examples.
Humanistic orientation
Among all the psychological currents that exist, humanistic orientation can be highlighted. Within humanistic psychology there are several authors, united by criticism of positivist psychology and supporters of a more human psychology. One of the main authors of humanistic orientation is Abraham Maslow. This psychologist spoke of a third force, opposed to the traditional psychoanalytic and behavioral approaches. Your model considers positive man Because, although he suffers, he is able to formulate projects, evaluations, options, and has Right to self -determination. Maslow's positions have given rise to the movement of human potential. You will find more information about Maslow's theories in the following articles: Theory of Maslow's needs and Maslow's human motivation theory.
Another author close to the humanistic position is Carl R. Rogers, American psychologist and founder of the Therapy focused on the client. In Rogersian psychotherapy it is the client, and not the therapist, who establishes the rhythm of march and decides the therapy goals. Rogersian psychotherapists call their client patients, and focus their attention on the current experience, trying to help the patient with a condescending attitude that should favor the self -realization and development of psychological potentialities.
The Palo Alto School
In the early 50s in Palo Alto, California, a group of scholars led by anthropologist Gregory Bateson, undertook a study on the forms of communication present in the families that had among their members an schizophrenic relative. The knowledge and theories of the School of Palo Alto, thanks above all to the systematization and dissemination made by one of the group members, Paul Watzawlick, have revolutionized theories about communication and have given new indications for the Psychotherapeutic treatment of families.
The approach of the Palo Alto school considers The family as a system and to the member as a carrier of the symptom that indicates the dysfunction of the system. Therapy cures the problem by changing family relationships and not the individual.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to The currents of psychology and its characteristics, We recommend that you enter our category of basic psychology.

