The mesolímbic route, structure and function
- 3865
- 1241
- Hugh Greenholt
Experience such simple things as feeling joy to see someone again that we want or feel pleasure when taking a good cup of coffee, it would not be possible if the different areas of our brain did not connect to each other through the neurotransmitter Dopamine, who travels by sending signals through different routes. One of those routes is the Mesolímbica, whose function is essential for our survival. Want to know more about her? In this article we talk about this important route of the brain.
Content
Toggle- What is the Mesolímbica route?
- Location of the Mesolímbica Via
- Main structures
- Mesolímbic route functions
- Disorders in which it is involved
- Bibliographic references
What is the Mesolímbica route?
The mesolmbic route is a brain route constituted by A set of dopaminergic neurons that connect different areas of the brain forming an essential circuit for our correct operation. This means that dopaminergic neurons send information to each other following a route thanks to dopamine, a very important neurotransmitter in our nervous system that allows signals to be sent between neurons related to the emotional, motor and cognitive responses of the organism to certain stimuli.
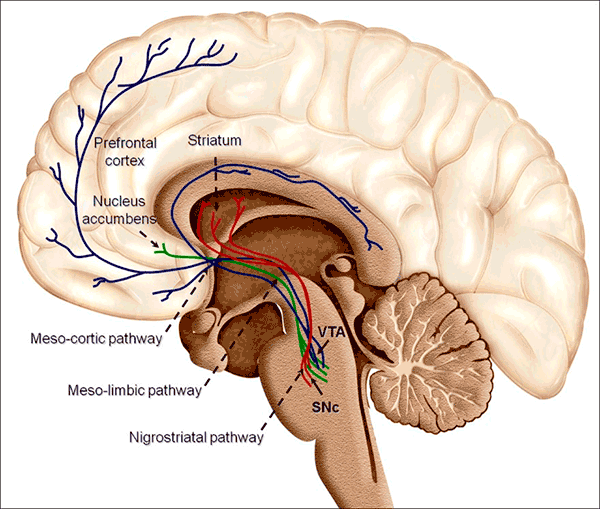
The Mesolímbica is one of the four main Dopaminergic pathways that exist in our brain, in addition to the Mesocortical route, route nigroestriatal and the Via tuberoinfundibular. These routes have in common the connection between different parts of the brain through dopamine transmission.
Location of the Mesolímbica Via
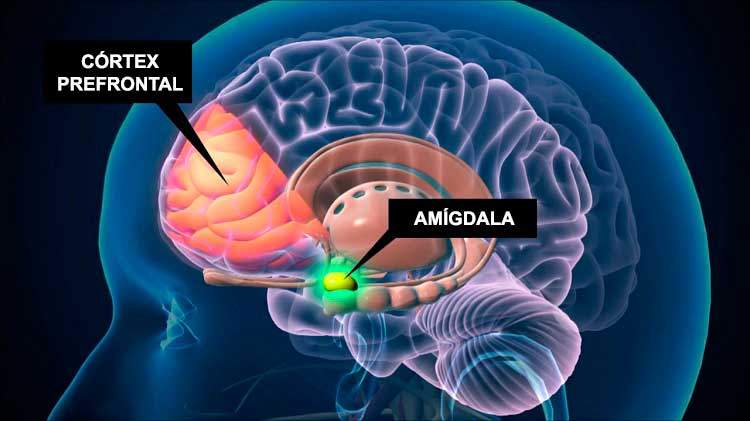
The mesolmbic route or route connects the midbrain with the limbic system. This occurs through the projection of dopaminergic neurons from the Ventral tegmental area, In the midbrain, with the ventral striated body, among which is the Accumbens nucleus. In addition, it is related to other structures such as amygdala, he hippocampus either The prefrontal cortex.
 Neurosthetic, how we process beauty
Neurosthetic, how we process beauty Main structures
These are some of the main components of the Mesolímbic route:
- Ventral Tegmental Area: Located in the midbrain, this structure contains dopaminergic, gabaergic and glutamergic neurons. It is one of the main dopaminergic areas and constitutes the headquarters of the body of dopaminergic neurons of the Mesolimbic system.
- Accumbens nucleus: Located in the ventral striatum, it is part of the limbic system and is composed mainly by medium spiny neurons. Its projections come from, in addition to the ventral tegmental area, the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala. Like the ventral tegmental area, it has a very important role in brain reward processes by increasing dopamine levels by receiving signals from these areas and creating pleasant and emotional responses among many other functions.
- Amygdala: The amygdala is an important structure formed by neuronal nuclei and located in the temporal lobe, which is part of the limbic system and whose main task is the processing and storage of emotions.
- Hippocampus: The hippocampus is a brain region located in the temporal lobe that has a main function in the memory and learning consolidation processes. An injury in the hippocampo would make unable creating specific memories.
- Prefrontal cortex: Located in the frontal lobe, the prefrontal cortex is the important area of our brain that is responsible for cognitive control, something like a director of our cognitive processes, which include problem solving, decision making or the attention. This is projected to many areas including the accumbens nucleus.
Mesolímbic route functions
The main functions of the mesolímbic route are related to the experimentation of the reward or pleasure, as well as the feeling of motivation and the Reinforcement or emotional learning. For example, when we feel sexual pleasure or experience motivation when going to a dinner with friends, the mesolímbic route would have a lot to do with these sensations.
The role it has in the Motivation towards pleasure and reward since when an injury occurs in this route, the motivation to achieve a low reinforcement. This route is very involved in the feeling of pleasure in the face of drugs and the experimentation of hallucinations and delusions.
Disorders in which it is involved
The mesolímbic route has an important role in different disorders such as drug addiction. When drugs that have produced high levels of dopamine on these roads are ceased.
In addition to other disorders such as depression or eating disorders, the mesolímbic route has a great role in schizophrenia. Specifically it seems that this route is associated with the positive psychotic symptoms, Especially auditory hallucinations and delusions, with great hyperactivity in the mesolímbic pathway, so when patients take drugs that decrease the amount of dopamine blocking dopaminergic receptors, positive symptoms are reduced or disappeared. This not only happens in schizophrenic patients but in other people who experience psychosis such as drug induced, mania or dementia.
Bibliographic references
- Llorente-Berzal, Á., & Maldonado, R. (2013). The Mesolímbica Via: Anatomy, Neurochemistry and Functions. Neurology Magazine, 57 (11), 521-530.
- García-Fuster, m. J., García-Sevilla, J. TO., & La Harpe, R. (2010). The mesolmbic path and addictive diseases. Neurology Magazine, 50 (8), 473-482.
- Moreno-Pérez, o., & Martínez-Fuentes, M. (2016). The mesolmbic path: paper in addiction and other psychiatric disorders. Neurology Magazine, 63 (11), 491-498.
- Aranda-Abreu, g. AND., & Hernández-Avila, C. TO. (2015). The mesolmbic path and its role in motivation and emotion. Neurology Magazine, 61 (9), 401-408.
- Gómez-Velázquez, f. R., & Becerra-Fernández, A. (2019). The Mesolímbica and Psychosis: Implications in Pharmacological Treatment. Neurology Magazine, 68 (9), 379-386.
- Olvera-Cortés, m. AND., & González-Pérez, M. N. (2018). The Mesolímbic route and the cerebral reward system: implications in addiction and depression. Mexican Neuroscience Magazine, 19 (2), 56-65.
- https: // psychopharmacologyinstitute.com/publication/The-Four-Dopamine-Pathways-Relevant-To-Antipsychools-Pharmacology-2096
- https: // www.Scientedirect.com/Topics/Neuroscience/Mesolimbic-Pathway

