Dopamine functions, imbalances and how to improve the levels of this neurotransmitter

- 1321
- 273
- Jeffery Jones
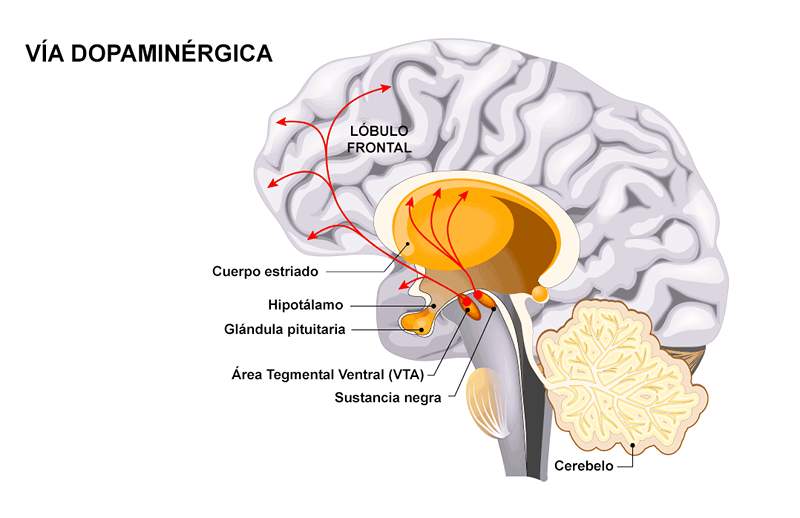
Dopamine is a Neurotransmitter released by the brain that performs numerous and important functions in our body. Dopamine occurs in dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the midbrain, in the black substance and the arched nucleus of the hypothalamus. This chemical plays an important role in motivation, pleasure, attention and learning, among other cognitive and emotional functions.
In this article we will explore in depth the role of dopamine in the human body and how it affects our mental and physical health. In addition, we will discuss how dopamine levels in the body can affect and how they can be balanced to improve our quality of life.
Content
Toggle- Dopamine function and its vital role in the human body
- How dopamine affects us
- What happens if there is excess dopamine in the body?
- What happens if there is low dopamine level in the body?
- When is released? Dopamine and pleasure as a reward
- Dopamine action areas
- Dopamine and addiction
- Dopamine and memory
- Dopamine and attention
- Dopamine and cognition
- Dopamine and creativity
- Dopamine and social relations
- Personality according to dopamine level
- Dopamine and psychosis levels
- Pain processing
- Dopamine and regulation of prolactin secretion
- Dopamine in nausea and vomiting
- What stimulates dopamine?
- Video: How to generate dopamine and improve well -being?
- Video: Dopamine fasting
- References
Dopamine function and its vital role in the human body
Some specific dopamine functions include:
- Regulates body movement, helping to control voluntary movements
- Promotes memory and learning ability, helping to remember important information.
- Regulates the reward system, providing a sensation of pleasure and motivation.
- Participate in behavior control, promoting people to look for goals and objectives.
- Improves attention and concentration.
- Regulates prolactin production, a hormone related to breastfeeding and stress.
- Influences the sleep cycle, helping to maintain a repair dream.
- Participate in the balance of the mood, regulating depression and stress.
- Collaborates in the learning process, helping to retain important information
However, an imbalance of dopamine levels can cause serious disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and drug abuse. Changes in dopamine levels can significantly affect the quality of life of a person. Therefore it is important to understand the function of dopamine and how it can be regulated to improve health and well -being.
How dopamine affects us
A part of the brain called Basal ganglia regulates movement. Basal ganglia, in turn, depend on a certain amount of dopamine to function with maximum efficiency. Dopamine action occurs through Dopamine receptors D1-5.
Dopamine reduces the influence of the indirect route and increases direct road actions within the basal ganglia. When there is A dopamine deficiency in the brain, The movements can be delayed and uncoordinated. On the other hand, if there is a Excess dopamine, The brain induces the body to carry out unnecessary movements, such as repetitive tics.
What happens if there is excess dopamine in the body?
When there is an excess of dopamine in the body, unwanted effects may occur. May include greater activity in basal ganglia, resulting in excessive and involuntary movements.
In addition, the Dopamine excess can also contribute to mental health disorders such as anxiety and schizophrenia. It can also cause greater impulsivity, difficulty regulating emotions and sensations of excessive pleasure. Therefore, it is important.
What happens if there is low dopamine level in the body?
When dopamine levels are insufficient in the body, adverse effects may occur. It can cause a reduction in the body's ability to control voluntary movements, which can lead to Lack of coordination and slow movements.
In addition, a lack of dopamine too can contribute to mental health disorders such as depression and mood disorders. It can also cause a decrease in the ability to feel pleasure and motivation, which can affect the quality of life. That is why it is important to maintain dopamine levels in an adequate range to avoid health problems. The treatment of low dopamine levels can include changes in diet, exercise, medication and therapy.
 Temporary lobes: Anatomy and function
Temporary lobes: Anatomy and function When is released? Dopamine and pleasure as a reward
Dopamine is the chemical that intervenes in the receptors of the pleasure of the brain. It is released in pleasant situations and stimulates the individual to go in search of what has provided him with this sensation. Here is mainly The food, sex and Drugs of abuse, since all of them stimulating dopamine release in the brain, particularly in areas such as the Accumbens nucleus and prefrontal cortex.
In fact, overweight has been related to the deficit of dopaminergic receptors in the subject's nervous system, which is why they seem to need to eat more food to notice the same satisfaction as other people.
Dopamine action areas
Dopamine and addiction
Cocaine and amphetamines inhibit dopamine reuptake.
Cocaine is a dopamine conveyor blocker that competitively inhibits dopamine collection to increase their presence in the recipients.
Amphetamine increases dopamine concentration in synaptic space, But through a different mechanism. Amphetamines are similar in structure to dopamine, and thus they can enter the presynaptic neuron through their dopamine transporters. Amphetamines force dopamine molecules to leave their storage vesicles. By increasing the presence of dopamine in the synaptic space, there is an increase in pleasant feelings and finally to addiction.
Dopamine and memory
The high levels of dopamine in the brain, especially the prefrontal cortex, Help in the improvement of working memory. However, this is a delicate balance, since both levels increase and reduce to abnormal levels, so memory ends up suffering.
Dopamine and attention
Dopamine helps concentration and attention. Dopamine helps to focus on vision, and this in turn helps direct attention to better. Dopamine also seems to be responsible for determining what remains in our short -term memory According to the information received. It is believed that reduced concentrations of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex contributes to the TDAH attention deficit disorder.
Dopamine and cognition
Dopamine controls the information flow of the frontal lobes of the brain and also from other areas. Dopamine disorders in this region lead to the decrease in neurocognitive functions, especially memory, attention and problem solving.
D1 D1 and D4 receptors are responsible for the improvement of cognitive processes. Some of the antipsychotic medications used in disorders such as schizophrenia act as dopamine antagonists. The so -called "typical" antipsychotics act more frequently in D2 receptors, while atypical drugs also act on D1, D3 and D4 receptors.
Dopamine and creativity
It has been observed that people with a minor density of D2 receptors of dopamine at a talamic level are more creative.
One of the tables of the thalamus is to filter the stimuli from the cerebral cortex. Apparently a smaller number of receptors would facilitate neuronal connections that allow us to associate concepts in a more efficient way, thus improving creativity.
Dopamine and social relations
Sociability is also closely linked to dopamine neurotransmission. A low collection and union of D2 of dopamine is often found in people with social anxiety or social phobia.
It is believed that some of the Negative characteristics of schizophrenia (Social withdrawal, apathy, Anhedonia) can be related to low dopamine levels in certain areas of the brain.
On the other hand, people with bipolar disorder in manic states become hypersocial, as well as hypersexuals. This is attributed to an increase in dopamine. Maniac states can be reduced with dopamine blockers such as antipsychotics.
Personality according to dopamine level
Some investigations show that the amount of dopamine found in the cerebral tonsil could be an indicator of the degree of nervousness or the usual tranquility of a person, as well as the confidence he has in himself or the tendency to be more or less fearful.
Another characteristic of personality that is affected by dopamine is Search for strong emotions. Apparently a greater presence of dopamine in certain brain regions influences having more "optimistic" or lack of danger assuming too high risks.
Can also help create a most motivated personality. People with higher levels of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex are more arranged and motivated to meet demanding objectives.
Dopamine and psychosis levels
The abnormally high dopaminergic transmission has been related to the psychosis and the schizophrenia. For this reason, antipsychotcos work largely due to dopamine inhibition at the receiver level.
Pain processing
Dopamine plays a role in pain processing at multiple levels of the central nervous system. This includes the spinal cord, periacueductal gray substance (PAG), the thalamus, the basal ganglia, the island cortex and the cingulated cortex. The low dopamine levels are associated with painful symptoms that occur frequently in Parkinson's disease.
Dopamine and regulation of prolactin secretion
Dopamine is the main Neuroendocrine inhibitor of the previous pituitary gland prolactin secretion. The dopamine produced by neurons in the arched nucleus of the hypothalamus is released in the hypothalamus-hyposary blood vessels of the average eminence, which supply the pituitary gland. This acts on the cells that produce prolactin. These cells can produce prolactin in the absence of dopamine. Dopamine is the inhibiting hormone of prolactin (PIH), or proactostatine.
Dopamine in nausea and vomiting
Dopamine is one of the neurotransmitters involved in the control of nausea and vomiting through interactions in the chemoreceptors activation zone. Metoclopramide is an antagonist of D2-receiver and avoids nausea and vomiting.
What stimulates dopamine?
Dopamine is released in the brain in response to a variety of stimuli, from delicious food and pleasant experiences to achievements and goals achieved. The brain reward system is closely related to dopamine levels, Which means that the activities and thoughts that are related to reward or pleasure will increase dopamine levels.
On the other hand, certain medications and drugs can also artificially increase dopamine levels in the brain, but it is important to remember that excessive use of these can cause serious problems. Although some studies suggest that exercise and meditation can help increase dopamine levels.
 Planned octopus suicide is related to a human genetic disorder
Planned octopus suicide is related to a human genetic disorder Video: How to generate dopamine and improve well -being?
Video: Dopamine fasting
References
- Bradford, h.F. (1988). Fundamentals of neurochemistry. Barcelona: Labor.
- Berridge K, Robinson T (1998). "What is the role of dopamine in reward: Hedonic Impact, Reward Learning, or incentive Salience?". Brain Res Brain Res Rev 28 (3): 309-69. PMID 9858756
- Carpenter, m. 1994. Neuroanatomy, foundations. Fourth edition. Pan -American Medical Editorial
- González, s. et al. CIRCADIAN-REALATED HETEROMERITION OF ADRENERGIC AND DOPAMINE D4 RECEPORS MODULATES MELATONIN SYNThesis and relaase in the pineal gland. PLOS Biology 10 (6), June 19, 2012
- Guyton, a. Anatomy and physiology of the nervous system. Basic neuroscience. Second edition. Pan -American Medical Editorial
- Schultz W (2002). "Formal getting with dopamine and reward". Neuron 36 (2): 241-263. PMID 12383780
- Uribe, c. Arana, a. Lorenzana, p. 1997. Fundamentals of Medicine. Neurology. Fifth edition. Corporation for Biological Research
- https: // movementDisorders.Online Library.Wiley.com/DOI/ABS/10.1002/mds.22020
- https: // academic.OUP.com/EDRV/ARTICLE-ABSTRACT/6/4/564/2548821?redirectedfrom = fulltext
- « Serotonin The hormone of happiness and an effective antidepressant
- What happens to our brain when we fall in love? »

