Opium and opiates, types and effects

- 1470
- 267
- Lorenzo West I
He opium It is a set of substances obtained from the seeds of the oky or real poppy plant. Opium has powerful narcotic properties and contains alkaloids, such as morphine or codeine.
Content
Toggle- EFFECTS OF OPIO
- History of opium
- Opioid opium
- How do opioids work?
- Bibliographic references
EFFECTS OF OPIO
The effects of opium are very strong, producing A state of analgesia and sensations of happiness, as well as general tranquility, although they can also generate vomiting, sweat, headaches, among others. In addition, it causes abstinence syndrome in which effects such as depression, nausea or diarrhea occur.
Its constituents and derivatives are used as analgesics in extreme circumstances, As in the terminal stages of cancer, although its production is also intended for the manufacture of illegal drugs considered very dangerous due to its high addiction capacity.

History of opium
Opium is known as one of the oldest drugs in the world. The most remote reference we have today about opium consumption comes from ancient Mesopotamia, during approximately 3400 ac. The ancient Sumerians, referred to the flowers of the poppy from which they extracted opium as "the plant of joy".
His cultivation was continued by the ancient Greeks, Persians and Egyptians, being their very remarkable use during the reign of Tutankhamun (1333-1324 AC). Homer already in the Odyssey, he referred to the huge healing powers of this narcotic.
Its consumption by ancient civilizations was used to help people sleep, relieve pain, soothe children and even as an anesthetic in operations. However, it is likely that they would also be used for recreational causes, without probably aware of its addictive effects.
Opium was probably introduced in China and East Asia in the seventh or VII and its trade has been and is so widespread that competitiveness for its control has caused conflicts such as Opium wars During the nineteenth century, they culminated in China's defeat. By 1900, it was estimated that in the US. UU. There were 200.000 opium addicts.
 Haloperidol, a widely used antipsychotic
Haloperidol, a widely used antipsychotic Opioid opium
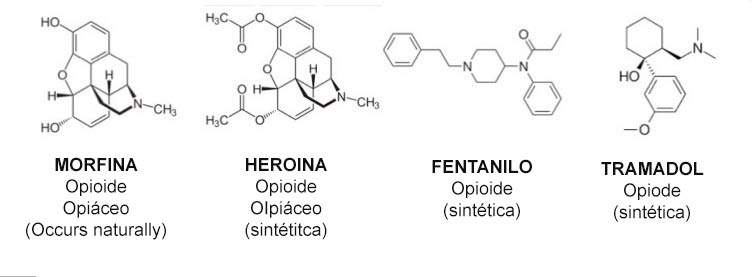
The opiates are psychoactive chemicals that come, either directly or indirectly, of the Simply plant and that mimic the analgesic power of Endogenous opiates, Those that our central nervous system produces on its own, known as endorphins, encephalins and dinorphins. These Exogenous opiates They are divided into three types according to their procurement and manufacturing:
- Natural opiates They are opium alkaloids. They come directly from the plant and are not synthetic. These are morphine, considered the main of alkaloids, codeine and tebaine.
- The semi -manthic/artificial opiates, They are created in laboratories from natural opiates. These can be hydrocodone, synthesized from codeine; the oxycodone synthesized from the tebaine; and heroin, synthesized from morphine and much more powerful than this.
- Synthetic opiates are completely artificial and mimic the effect of the previous ones, although their structure It is not related to opium alkaloids. These can be Petidine or Methadone.
How do opioids work?
In the central nervous system of humans and animals, there are opioid receptors. When we consume opioids, these They join these receptors Blocking pain perception. In addition, they cause feeling of well -being, although also side effects such as nausea or drowsiness.
Opioids make the nervous system release dopamine, neurotransmitter considered as Pleasure Center and that discharges in the brain the immediate sensation of euphoria and reward. This generates one High motivation, causing the consumer to need new doses to get that satisfaction discharge again. Its continued use, generates a high tolerance to the substance and causes a very dangerous addiction.
Consuming opium or its derivatives, without medical and pharmaceutical supervision, can be very dangerous. The use of opium -derived medications is extremely limited by its High risks of addiction, being many of them illegal. The consumption of medications such as morphine is restricted to medical opinion and are only used when a medical professional considers it appropriate given its properties to relieve pain. However, the high addiction generated by these substances and dire health consequences They can carry. Continued consumption of illegal derivatives such as heroin, continue to cause suffering and loss of thousands of lives.
Bibliographic references
- Velázquez, a., & Carbajal, D. (2017). Basic and clinical pharmacology. Mexico: McGraw-Hill Education.
- Bobes Garcia, J., & Sánchez, J. (2018). Drugs and addictions. Madrid: Pan American Medical Editorial.
- EMCDDA. (2019). European Drug Report 2019: Trends and Developments. The Lancet Psychiatry, 6 (10), 781-783.
- Jiménez Murillo, L. M., & García-Salido, to. (2018). Basic Toxicology Manual. Madrid: Panamerican Medical.
- Martins, s. S., Sampson, l., Cerdá, m., & Galea, S. (2018). Worldwide Prevalence and Trends in an intentional Drug Overdose: A Systematic Review of the Literature. American Journal of Public Health, 108 (10), E1-E11.
- Samhsa. (2021). KEY SUBSTANCE USE AND MENTAL HEALTH INDICATORS IN THE UNITED STATES: Results From The 2020 National Survey On Drug Use and Health. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
- « What happens when we deny our feelings
- What is cinophobia or irrational fear and how to correct it »

