The spinal bulb knows its characteristics and vital functions
- 4647
- 1539
- John Von
The nervious system It is a complex organization of interconnected structures and systems that work together to allow us to interact with the world around us and perform vital functions for our survival. One of the most important parts of this system is spinal bulb, A crucial structure of the brain that plays a fundamental role in the regulation of vital processes such as blood pressure and breathing, and in the coordination of multiple body functions. Understanding its function and relationship with the rest of the nervous system is essential to understand how the body works and to prevent and treat health -related problems.
Content
Toggle- What is the spinal bulb?
- Spinal bulb
- How is it formed? Spinal bulb structure
- Spinal bulb functions. That controls?
- Relationship with spinal cord and brain
- Importance of maintaining a proper functioning of the spinal bulb
- Spinal bulb problems and its consequences
- How can the spinal bulb be damaged?
- Conclusions
- Links of interest
What is the spinal bulb?
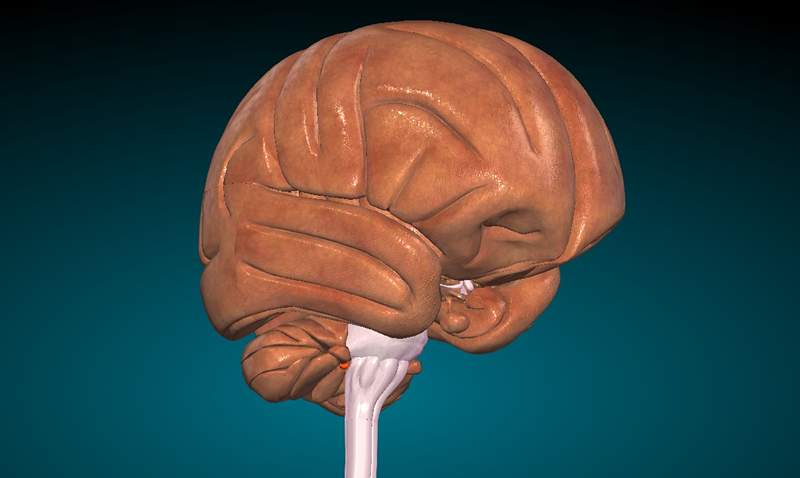
The spinal bulb is the most caudal structure of the brain trunk. It is a rounded bump, composed of white matter and gray matter that functions as the main connector between the spinal cord and the central nervous system.
The spinal bulb is divided into different areas. A medium fissure in the anterior area connects this structure with the spinal cord. On both sides of the bulb are the pyramids, the most important area in this structure, which connect the bulb with the spinal cord. Outside is the pre -collend groove. The spinal bulb is also the center where the nerves are found on one side and another of the brain, that is, the meeting point between one hemisphere and another.
Spinal bulb
He spinal bulb, Also known as a oblong medulla, it is located in a key zone of the nervous system: between the brain trunk bridge at the top and spinal cord in the lowest area. Previously it is placed in front of the cerebellum and its important location manages to connect the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system, with the central nervous system. That is, it is the connection point between muscles and body organs with the brain. This does it by transferring the information that comes from the peripheral nervous system to a structure called Tálamo, which selects the stimuli that will be subsequently transferred to the rest of the brain according to its importance.
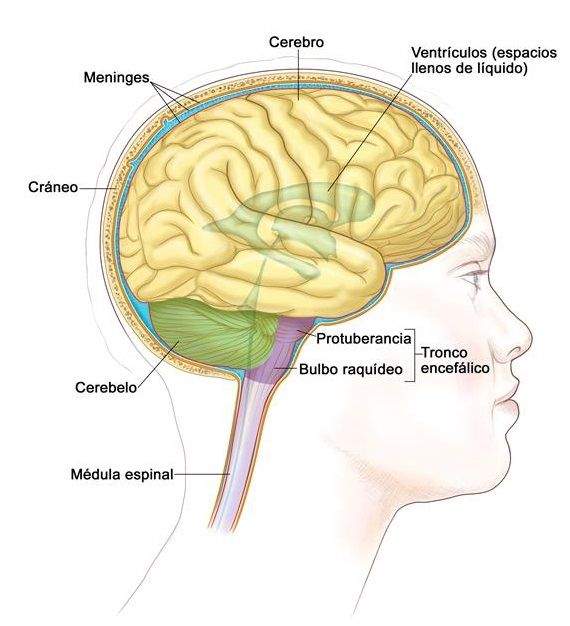
Also, too Connect the two cerebral hemispheres whose nerves are in this structure, so an injury on one side of the bulb can cause the opposite hemisphere to present problems.
The spinal bulb receives oxygen through different arteries, such as the anterior spinal artery, the lower rear cerebean artery and direct branches of the vertebral artery.
 What is catalepsy?
What is catalepsy? How is it formed? Spinal bulb structure
Spinal bulb is a complex structure formed by different types of nerve tissues (myelinized nerve fibers), including white matter and gray matter. White matter is responsible for nerve signal transmission, while gray matter contains nerve cells responsible for processing and transmitting sensory information. In addition, the spinal bulb is made up of numerous nerve fibers that connect different regions of the brain and allow the coordination of body and mental functions. In summary, spinal bulb formation is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
Spinal bulb functions. That controls?
The spinal bulb is involved in different involuntary functions and due to its connector paper between the spinal cord and the brain, its importance is key to the survival of the human being, carrying out actions such as: for example:
- Control of autonomous functions
- Coordination of involuntary body movements (for example, swallowing, sneezing, nausea, among others)
- Control and coordination of voluntary movements (for example, movement of the head, speak)
- Respiratory control
- Cardiovascular control (heart rate regulation and blood pressure)
- Control and regulation of visceral and gastrointestinal functions
- Transfer of sensory information between the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system
In summary, spinal bulb is a fundamental structure of the nervous system that plays a key role in many of body functions. This structure coordinates the activity of different parts of the body and allows our body to function efficiently.
Relationship with spinal cord and brain
The spinal bulb is a key connection point between the spinal cord and the brain. The spinal cord is responsible for the transmission of nerve impulses from the body to the brain, while the spinal bulb is responsible for coordinating and regulating these impulses. In addition, the spinal bulb also sends nerve impulses from the brain to the spinal cord, allowing efficient bidirectional communication between these two critical structures of the nervous system.
 The somatic nervous system (SNS), anatomy and function
The somatic nervous system (SNS), anatomy and function Importance of maintaining a proper functioning of the spinal bulb
The proper functioning of the spinal bulb is essential for health in general, since this structure plays a key role in many of the body functions, including breathing, cardiovascular control and coordination of body movements. In addition, a spinal bulb in good condition is essential for the transmission of sensory information and to maintain effective communication between the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. Therefore, it is important to maintain a proper functioning of the spinal bulb to guarantee good health in general.
Spinal bulb problems and its consequences
Problems and injuries in this structure can cause different difficulties related to many SENSITIVE AND COORDINATOR SYSTEMS. These can translate into problems in tasting, movement, breathing or even heart rate.
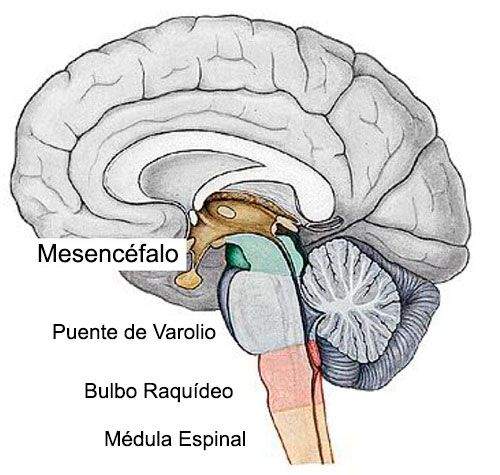
As we have explained above, the spinal bulb is involved in many important physical processes, such as breathing and even the diameter of arteries and veins, sneezing or even swallowing. That is why damage to this structure can interfere in crucial functions, giving rise to problems such as:
- Paralysis
- Vertigo
- Swallow problems
- Problems to make movements like turning the head
- Respiratory difficulties
- Loss of muscle coordination
- Being a meeting point between the two hemispheres, damage to one side of the spinal bulb can cause problems on the other side of the body.
How can the spinal bulb be damaged?
Substance abuse such as opiates can have a negative impact on spinal bulb, inhibiting its operation and putting at risk the ability to breathe and maintain normal heart rate. In severe cases, this can be deadly. In addition, since the spinal bulb is a key communication point between the nerves of each hemisphere and the nervous system, any damage to this structure can negatively affect the normal functions of the body.
 What are neurosciences and differences with neurology
What are neurosciences and differences with neurology Conclusions
The spinal bulb is a critical structure in the anatomy of the organism, in charge of regulating vital functions such as breathing and heart rate. It is composed of white matter and gray matter and is at a lower cranial level than the oblong medulla. In addition to being the meeting point for the nerves of each hemisphere, the spinal bulb is also responsible for controlling the cranial nerves, such as the Vago dorsal nerve and the hypogloso nerve. The gray substance of the medial region is essential for the functioning of these nerves, while the white substance of the ventral region is essential for nerve tracts that are responsible for transmitting information up and down in the nervous system. In conclusion, the spinal bulb is a fundamental component for the proper functioning of the organism.
Links of interest
- Oblongata Medulla. https: // brainmadesimple.com/medulla-oblongata/
- What is the medulla oblongata? (2018). https: // www.Thoughtco.com/Medulla-Oblongata-Anatomy-373222
- Oblongata Medulla. https: // www.Healthline.com/Human-Body-Maps/Medulla-Oblongata#1

