Exercise your memory with the Dual Dual N-Back of Cognitive Training
- 1214
- 285
- Herbert Ritchie
The Dual N-back memory test is a task linked to the working memory that is used to evaluate and train a person's ability to retain and manipulate information in short-term memory.
Content
Toggle- What is the Dual Dual N-Back of Cognitive Reinforcement
- The different modalities of the N-back test
- How dual N-back test works
- The benefits of the Dual N-back test
What is the Dual Dual N-Back of Cognitive Reinforcement
In the N-back test, different stimuli sequences are presented, such as letters, numbers, colors or shapes, and The participant must identify whether the current stimulus is identical to the one presented previous essays, so that the greater the value of N, the higher level of difficulty since it is necessary to remember the last n stimuli.
Unlike the simple N-back version in which you work with a single stimulus, in the dual version, you have to monitor two sequences of different stimuli at the same time, which increases the degree of difficulty. In each test trial, two stimuli are presented and the participant must indicate if any of those stimuli is identical to the one presented.
The Dual N-back memory test is frequently used in research studies to evaluate the effectiveness of different cognitive interventions and to examine individual differences in short-term memory capacity and working memory. In addition, it has also been used in research on neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as attention deficit disorder and hyperactivity (ADHD), schizophrenia and mild cognitive deterioration.
The different modalities of the N-back test
In the classic version of the N-back test, 48 letters are shown for 2 minutes. If we work with n = 1, the objective will be to detect if the letter that has just been shown coincides with the one that appeared just before. For n = 2, it will be necessary to detect if the last letter shown coincides with the one that was shown twice and so on for n = 3, 4 and 5.
In psychoactive we present a much more complete version in which you will have 4 different modalities according to the number of stimuli to be remembered:
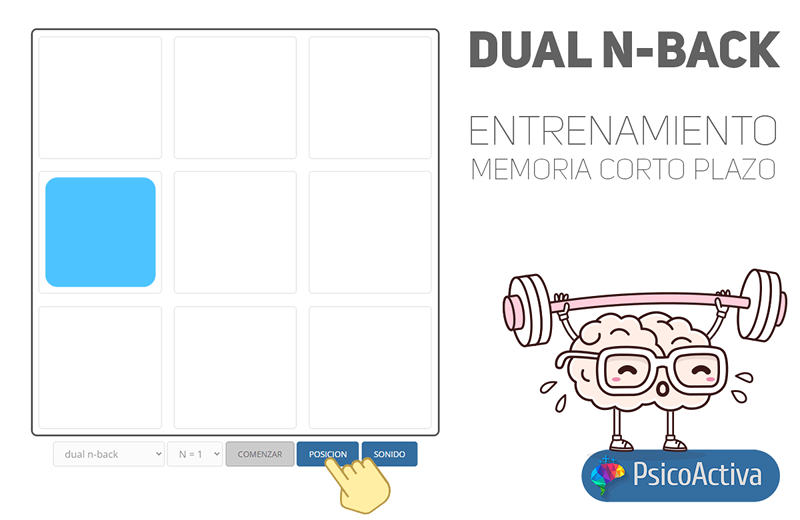
- N-back: It is an adaptation of the classic version in which there is a single stimulus to remember that it is the position of the figure on the 3 × 3 board. The objective of the test is to press the position button when the figure appears in the same position in which it was previously shown, taking into account the value of n selected.
- Dual N-back: In the dual n-back version, two stimuli must be memorized at the same time, which are the position and sound that accompanies it. If any of the stimuli is repeated taking into account the value of N, the corresponding position or sound button will have to be pressed.
- Triple N-back: Similarly, in the triple N-back version, three simultaneous stimuli are shown, which are the position, sound and color of the figure. Therefore, we will have to press the position, sound, or color button according to the stimulus that is repeated.
- Quadruple N-back: Finally, the most difficult level, the Quadruple N-back test. In this case, four stimuli will have to be memorized simultaneously and press one of the four buttons: position, sound, color or shape, according to the stimulus that is repeated.
Long -term memory tests with interference
How dual N-back test works
The operation is very simple. Select the type of test you want to perform among the 4 available: N-back, dual N-back, triple N-back or quadruple N-back. Indicate the number of steps back to remember and press the Start button.
Each stimulus will be displayed for a brief period of half a second followed by a 2 -second pause. During all that time it will be possible to press any of the response buttons when a coincidence occurs in the stimulus corresponding to the button.
For example, if you select the modality "Dual N-back" with "N = 1", You will have two buttons: position and sound. In each iteration of the test, a figure will be shown in one of the nine boxes accompanied by a sound. If the position of the figure that is being shown coincides with the position of the figure that was shown just before, you must press the position button, if it is the sound that coincides, you must press the sound button and if neither of the two of the two does not match , do not press any button.
At the end of each exercise, your successes, failures and omissions will be shown under the game. These results are accumulating, which will help you verify your progress.
We recommend you start the test "Dual N-back" and the value "N = 1", and increase the degree of difficulty as your results are improving. Keep in mind that the maximum difficulty option achieved with mode "Quadruple N-back" and "N = 5" It is extremely difficult.
Be sure to have your speakers activated.
And you, what are you waiting for to improve your memory in the short term? N-back dual N-back triple N-back quaruple n-back n = 1 n = 2 n = 3 n = 4 n = 5 start
| Departure | Mode | N | Successes | Failures | Omissions |
The benefits of the Dual N-back test
The N-back test was designed by Wayne Kirchner in 1958 with the aim of measuring a person's ability to maintain and manipulate information in short-term memory. However, It has been shown that the regular practice of this task can lead to an improvement in working memory and short -term memory.
Regular N-back test can improve a person's ability to maintain information in short-term memory and manipulate it effectively. This improvement is due to neuronal plasticity, which is the ability of the brain to change and adapt to new demands. When the N-back test is practiced, working memory is being exercised and, over time, the brain improves this capacity.
In addition, the practice of N-back test can also improve a person's ability to concentrate and pay attention, which can be beneficial for other areas of daily life that require the ability to maintain and manipulate information in short memory term, such as study, work and daily tasks.

