Kegel exercises for women, what are, benefits and how to make them

- 1213
- 52
- Josh Runolfsson II
The pelvic floor is a muscle fibers that aim to protect the pelvis from possible detachment. For proper functioning of the pelvic soil, its constant strengthening is necessary throughout life.
Due to social taboos, most women do not know how to exercise this part of their body and end up suffering consequences such as incontinence, prolapsses or difficulties in enjoying sexual relations. For this reason, then we explain the importance and functioning of Kegel exercises, necessary for the maintenance of good sexual health.
Content
Toggle- Sexual health improvement
- Pelvic soil weakness
- How to do Kegel exercises?
- How to perform step by step exercises
- Bibliography
Sexual health improvement
In past times, sexual health was believed only covered the advice and care on reproduction and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. However, From 1974, WHO began to consider the integration of somatic, emotional, intellectual and social elements as part of sexual health.
Currently, the definition of sexual health focuses on care for pleasure and the right to information for free sexuality.
Under the definition above, sexual health is closely related to emotional and mental well -being. That is to say, Enjoying a satisfactory and riskless sex life is necessary to maintain health at the psychological level. Meanwhile, sexual health includes practices such as assistance during childbirth, safe abortion, gender violence prevention, sterility treatment and promotion of physical well -being in relation to sexuality.
In this sense, Physical problems such as sexual dysfunctions, urinary incontinence and lumbar pains generate difficulties for a full enjoyment of sexual relations. In general, these symptoms in women are related to weakness in the pelvic floor, which can be corrected through Kegel exercises.
Pelvic soil weakness
The pelvis is an anatomical region that houses various organs of the reproductive, urinary and digestive system. In order to protect this area of the body, the pelvis has a base made up of various muscles and ligaments, called pelvic floor. In this way, this base allows the control of sphincters, avoiding incontinence and prolapsses. So, There are several factors that can weaken the pelvic floor, such as high -impact sports or pregnancy processes.
For many women, the weakness of the pelvic soil can be reflected in the difficulty in feeling orgasms or pain in sexual relations. However, the strength of the pelvic floor also varies to the extent that we exercise the muscles of this area. Therefore, there are practices such as Kegel exercises, which have proven to be very beneficial to maintain good sexual health. Thus, Kegel exercises for women reduce incontinence, pelvic pain, improve blood circulation to the vagina and increase vaginal lubrication.
 Sleep paralysis, what is and why
Sleep paralysis, what is and why How to do Kegel exercises?
To begin the practice of these exercises, it is necessary to identify the pelvic soil muscles in order to carry them out properly. To achieve this we can imagine that the muscles it would use to stop the urine jet, these are the pelvic floor muscles are urinating and tightened. Also, the tip of a clean finger can be introduced in the vagina and tension the pelvic floor muscles around the finger. We should feel that the vagina is tension and the pelvic floor moves upwards. Therefore, The muscles of the abdomen, the legs or the buttocks should not be tension when we counter the pelvic floor muscles.
Having identified how to work the pelvic floor, we will place ourselves in a comfortable position so that your body relaxes, in bed or in a chair. They can be done in any position in which one feels comfortable. The first step would be to inhale on the nose deeply until the abdomen expands while filled with air. Subsequently, you have to exhale slowly through the mouth keeping the muscles of the pelvic floor tense from 3 to 6 seconds while exhaling.
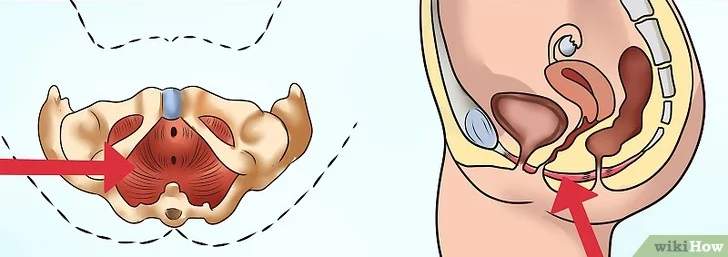
How to perform step by step exercises
- Identify the correct muscles: To do this, try to stop or reduce urine flow halfway during urination. If you succeed, you have correctly identified the pelvic floor muscles. Do not do this regularly, since it could affect your ability to urinate. Just use it as a way of learning to recognize the muscles you should exercise.
- Adopt the correct position: You can do these standing, sitting or lying exercises. When you are starting, it can be easier to make them lying or sitting.
- Contraction and relaxation: Squeeze (contract) the pelvic floor muscles, keep the contraction for five seconds and then relax for five seconds. Try to do it four or five times in a row. Work until the contraction is maintained for 10 seconds at the same time.
- Keep your concentration: To get the best results, focus on squeeze only pelvic floor muscles. Be careful not to flex the muscles of your abdomen, thighs or buttocks. Avoid containing breathing. Instead, breathe freely during the exercises.
- Repeat three times a day: Aims to make at least three series of 10 repetitions a day.
This exercise can be repeated 10 times per session. To get the best results, make 2 or 3 sessions of Kegel exercise every day. The sessions must be distributed during the day for greater efficiency.
It is important to highlight that the pelvic floor can be exercised since childhood, there is no ideal age to carry out the Kegel exercises. Unfortunately, the taboos imposed by our society regarding sexuality encourage ignorance towards these practices so necessary for sexual health maintenance. Unfortunately, Most women discover Kegel exercises only after having suffered the consequences of pelvic soil weakening. However, the ideal is to be carried out from youth with a preventive purpose, rather than rehabilitative.
Anatomy of the reproductive system and sexual organs
Bibliography
- Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. (2019). Exercises for pelvic floor muscles (kegel) for women. Education for patients and caregivers. Extracted from: https: // www.MSKCC.org/es/PDF/Cancer-Care/Patient-Education/Pelvic-Floor-Muscle-Kegel-Excise-Females
- World Health Organization. (2018). Sexual health and its relationship with reproductive health: an operational approach. Extracted from: https: // apps.quien.INT/IRIS/BITSTREAM/HANDLE/10665/274656/978924351284-SPA.PDF
- « Psycholinguistics, the study of human language
- Kegel Exercises for men, benefits and commeraalize them »

