Difference between temperament, character and personality
- 2581
- 372
- Perry Hirthe
This trio of terms acquired relevance within the nascent psychology on horseback between eight hundred and nine hundred through two different channels: "physiological" psychology on the one hand and psychoanalysis by the other. Throughout the history of psychology, in fact, the term personality was preceded by the term temperament, first, and the term character, then. Temperament-character-personality succession allows you to read very clearly the gradual step of a physiological conception to an increasingly psychological conception, and then integrate the whole into a global optics. In this Psychology-online article we will see the D togetherIFERENCE BETWEEN TEMPERAMENT, CHARACTER AND PERSONALITY.
You may also be interested: culture and personality in psychology index- What is personality
- What is temperament
- What is the character
- Differences between temperament, character and personality
What is personality
In common use, the meaning of the term personality can be identified with social skill or insight, evaluating the personality of an individual based on their ability to act positively in contacts with different people and in the most varied circumstances.
A second meaning considers inherent to the personality of an individual the most intense and living impressions that it raises in others; The reaction of the neighbor to the way of interacting an individual defines his personality: for example, arrogant, fascinating, difficult, etc.
Personality can still be understood as set of the qualities and characteristics of a subject, I mean, like sum of its biological and psychic aspects susceptible to observation and objective description, abstracting interpersonal reflexes.
In other definitions, the personality concept includes the unique, unrepeatable or most representative aspects of an individual. In short, the personality is the set of terms that are used to describe the individual, terms chosen based on different variables and dimensions, according to the field of interest of the student.
What is temperament
Speaking of temperament, we connect to the Innate psychophysical base, still focused on structure biological, of the provisions and peculiar trends of each individual to act in the world, to react to the environment and to behave, with special reference to the affective sphere. In this article you can find the types of temperaments with examples.
Temperament must be considered difficult, or at all, modifiable. Although life experiences, the particular characteristics of interpersonal relationships and family relationships, as well as the commitment of will to determine their own social position, the adventures of existence, frustrations, justifications, the different possibilities of realizing, In a word, the infinite existential circumstances affect temperament, making the subject assume modalities of behaving and reacting even different from innate, do not produce alterations, but interact with complex modalities, guiding the character construction of the individual.
What is the character
The character represents the Result of the interaction between temperament and environment: It is not, therefore, a static component of personality, but rather a dynamic component that is modified over time and with the vicissitudes of life that make up its aspects. This modifiability of character, on the other hand, is relative, possible in some expressions, but not in its deep nucleus; Also in the concept of character a component of usual and predictability is inherent, as an aspect not rigidly permanent. However, it has persistence.
The character, in addition, is so much less modifiable the more it progresses with age: there is talk of evolutionary age, which ends with maturity, to underline the still wide possibility of modification of the character, their own, of young people.
In the following article you will find the different types of character of a person.
As we have seen, character, personality and temperament are very related aspects and with certain differences. Next, we will see exactly what personality, temperament and character differ.
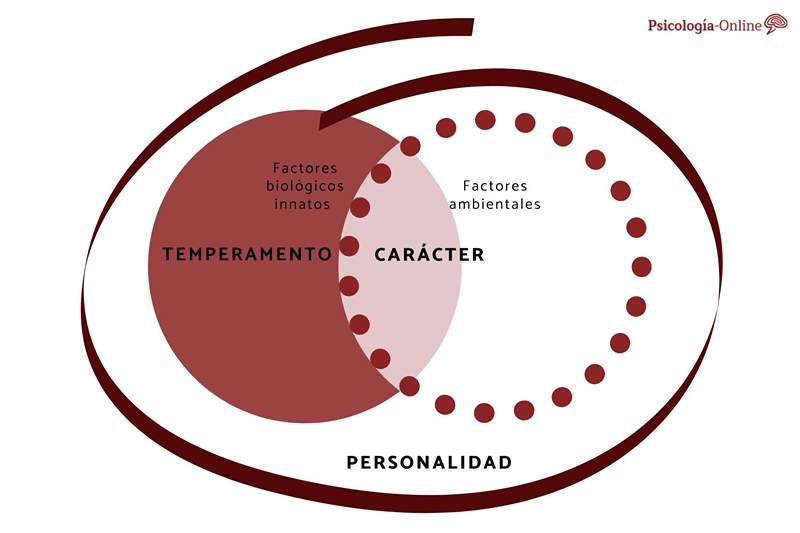
Differences between temperament, character and personality
Every human person has a biological foundation from birth: the innate organic heritage that each receives through hereditary transmission (hereditary constitution), from which the forms and proportions of the body (morphological constitution) and vital functions (circulatory , respiratory, digestive, etc.) dependent on the nervous and endocrine system (physiological constitution).
- The set of these elements determines an initial psychic structure or temperament: initial because to the conditioning of the hereditary factors The due to the environmental factors, affecting the whole life of the subject.
- Personality is the result of these "external" conditioning and the reaction to these conditioning.
- With the word temperament, the natural psychic response is understood to the hereditary organic set: express impulses, instinct trends, dispositions, affective states, etc.
- The character, on the other hand, is the result of the subject's initiative under the influence of the environment. In the child the character is not yet distinguished from the temperament, the decision is not distinguished from the impulse, the inhibition processes are poorly developed, the mental schemes are too simple, etc.
- Personality not only unifies biological aspects of temperament and psychic aspects of character, influenced by the environment, but also creates values, behavior models, forms of social organization capable of modifying the environment and the personality itself.
This article is merely informative, in psychology-online we have no power to make a diagnosis or recommend a treatment. We invite you to go to a psychologist to treat your particular case.
If you want to read more articles similar to Difference between temperament, character and personality, We recommend that you enter our category of basic psychology.
- « What is classic conditioning and examples
- Theory of learning by observation what is and examples »

