Entorrinal cortex we reveal your secrets
- 2720
- 540
- Hugh Greenholt
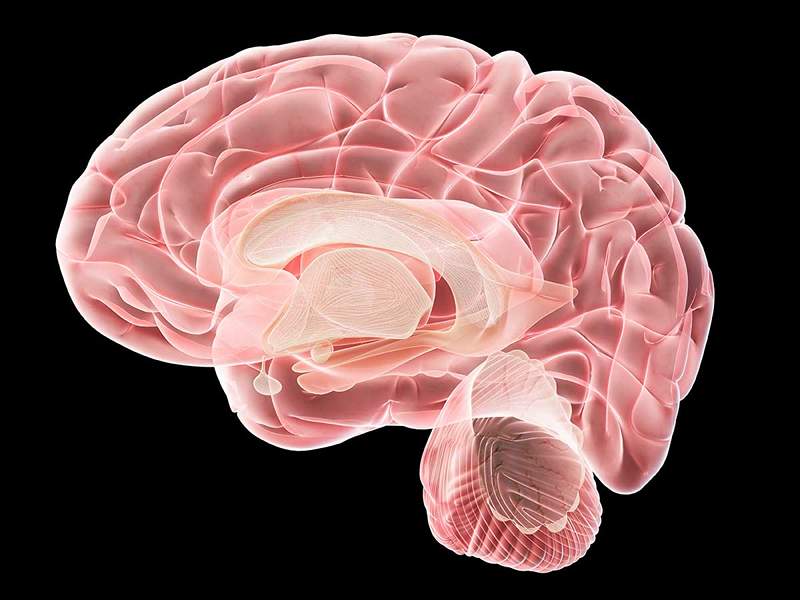
The Entorrinal cortex It is located in the medial temporal lobe and serves as a connector between the hippocampus and the neocortex. It performs extraordinarily important functions face the consolidation of autobiographical memory (the one that allows us to know who we are). Similarly, it is involved in declarative, procedural and spatial memory processes.
Also, it is believed that significantly influences memory consolidation and optimization during sleep. Undoubtedly, this small anatomical zone, little known, is of an outstanding relevance in regard to our executive and cognitive functionality. Let's see it more thoroughly.
Content
Toggle- Importance and characteristics of the entorrinal cortex
- Functions of the Entorrinal Cortality
- 1. It is a connector
- 2. Consolidated memory
- 3. The power of gnosis
- 4. Multimodal associations
- 5. Spatial Orientation
- 6. The power of smells
- CONCLUSIONS ABOUT THE ENTORRINAL CORTURE
- References
- Functions of the Entorrinal Cortality
Importance and characteristics of the entorrinal cortex
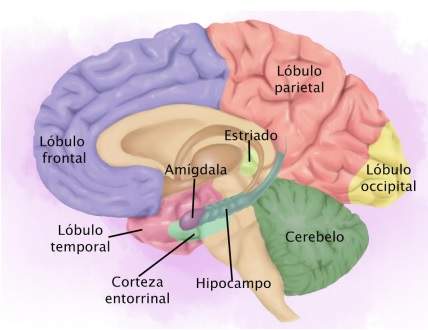
Intimately connected to the hippocampus, deeper warehouse of our memory, also has countless connections with different brain areas. Above all, it connects with important sensory pathways such as visual and olfactory. In addition, it is related to structures of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes.
However, the most important thing is that Entorrinal cortex It makes connector between the hippocampus and other areas of the brain. That is to say, It serves as a passage and filter station or distributor of the information between and leaves it.
The entorrinal cortex, being an integral part of the limbic system, receives afferences from the amygdala, providing memories of the emotional character so characteristic.
An example of this function the call Phenomenon of congruence emotion-thought. That is, when we are sad, we usually remember sad events of our step. The opposite happens when we are happy. Similarly, The conscious memory of a certain kind of happy or sad events can influence our emotional state. This fact would be a more expensive evidence of cognitive psychology.
Functions of the Entorrinal Cortality
The importance of this small structure is notorious, Well, it allows to make and integrate a good number of cognitive functions, Without which our conscious and proactive experience would be widely diminished, namely:
1. It is a connector
Indeed, Connect the hippocampus with other structures of the limbic system and the neocortex, allowing a broad and detail experience of the events stored in memory. They give them meaning, places them in time and context, It gives them meaning and wraps them with emotional content.
2. Consolidated memory
Experimentally it is known that lesions in the entorrinal cortex hinder, hinder and prevent memories consolidation, producing an amnesia.
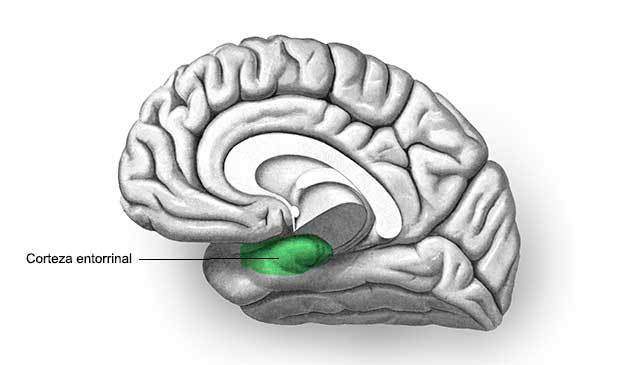
Therefore, the importance of this structure in the face of the consolidation and strengthening of memories is essential. In the same way, it is known that it is active during sleep, especially during the PHASE REM, which allows to consolidate the learning made during the vigil in our night rest hours.
3. The power of gnosis
The Entorrinal cortex Not only consolidates learning and memories, he also participates in the recognition of stimuli. It is closely linked to semantic memory, which tells us exactly what we see, hear, we touch, smell, we experience ... this quality It allows us to recognize the things that surround us and put them in context In the external world.
4. Multimodal associations
the Entorrinal cortex has an important associative power. Is able to integrate auditory and visual information, producing a more complete and deep sensory experience of reality.
5. Spatial Orientation
This little structure also allows us to guide ourselves especially, Without prejudice to the parietal lobe. It allows establishing relationships between external stimuli and memory, promoting the creation of mental maps, which allow us to memorize itineraries and know where we are going or what direction we should take.
6. The power of smells
We have all experienced ... there are smells that evoke memories. Did you know that the entorrinal cortex is directly involved in this phenomenon? Specifically, It is able to encode the intensity of smells and associate them with specific memories.
In this way, a concrete smell can make us recover an event of our life that we thought we forgotten, with an incredible amount of details. We can testify again of experiences and memories that we thought were forever.
CONCLUSIONS ABOUT THE ENTORRINAL CORTURE
In conclusion, the Entorrinal cortex It is a small structure without which our conscious and unconscious experience, our cognitive skills and executive functions (https: // pdfs.Semanticscholar.Org/F6F1/B7EC7671AFEA34CB9CFAE7804EE13C36936.PDF) would be seriously affected. Its function is to serve as a connector and work multimodal In the integration of sensations, emotions, memories and thoughts.
Perirrinal cortex, structure and function
References
- Capdevila, v., Almaguer-Melian, w., Rosillo-Martí, J. C., Vallejo, a., Sánchez, m. R., & Bergado-Rosado, J. TO. (2003). Comparative study of bilateral entorrinal cortex and fimbriaFóix lesion. Neurology Magazine, 37(7), 619-622.
- Pepper, h. J. (2004). The cerebral cortex beyond the cortex. Colombian Psychiatry Magazine, 33(1), 58S-75S.
- Solís, h., & López-Hernández, and. (2009). Functional neuroanatomy of memory. Neuroscience archives, 14(3), 176-187.

