Circunvolutions and cerebral furrows, anatomy and function
- 696
- 168
- Herbert Ritchie
The brain has a unique appearance that consists of many folds with turns, grooves or clefts. A cerebral fold is known as circumvolution, while depression is called groove or fissure.
The cerebral cortex contains numerous circumvolutions that are surrounded by one or more grooves. Circunvolutions and furrows give the brain their crumpled appearance. The cerebral cortex is the most developed area of the brain and is responsible for upper brain functions, such as thinking, planning and decision making.
Circunvolutions and grooves function
Circunvolutions and brain grooves fulfill two very important functions, these folds They help increase the surface of the cerebral cortex. This allows more neurons to accumulate in the cortex and therefore increases the ability of the brain to process information.
The turns and grooves also form brain divisions creating limits between the lobes of the brain and dividing the brain into two hemispheres. In turn, the cerebral cortex is divided into Four lobes. The frontal lobes are in the most front region of the cerebral cortex. The parietal lobes and the temporal lobes are behind the frontal lobes, with the parietal lobes located above the temporal lobes. Finally the occipital lobes are located in the posterior region of the cerebral cortex. Each of these brain lobes is responsible for several important functions. The frontal lobes are vital for control, thought and motors reasoning. Parietal lobes process sensory information, while occipital lobes are the main centers for visual processing. Temporary lobes are important for the production of language and speech, as well as for memory and emotion processing.
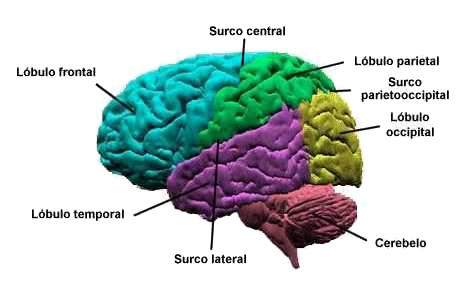
The grooves or brain cracks
Below is a list of several key grooves in the brain.
- Interhemispheric (medial longitudinal fissure): It is a deep groove in the center of the brain that separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The callosum is inside this fissure.
- Central groove (Rolando's fissure): It is a fissure that separates the parietal and frontal lobes.
- Side groove (Silvio's fissure): It is a deep groove that separates the parietal and temporal lobes. This fissure separates the fusiform circumvolution and the hypocampal circumvolution on the lower surface of the temporal lobes.
- Parietooccipital groove: It is a deep crack that separates the parietal and occipital lobes.
- Calcarino groove: This groove is located in the occipital lobes and divides the visual cortex into two.
 Brain food
Brain food The cerebral circumvolutions
A series of important circumvolutions of the brain are listed below.
- Angular circumvolution: It is a fold located in the parietal lobe that helps in auditory and visual processing, as well as in the understanding of language.
- Borca turn or area: brain area located in the left frontal lobe in most people who control the motor functions related to speech production.
- Cingulate turn: A arch fold in the brain located on the corpus callosum. It is a component of the limbic system and processs sensory information related to emotions and regulates aggressive behavior.
- Fusiform turn: Circunvolution located in the temporal and occipital lobes consisting of parts: lateral and medial. It is believed to play a role in facial recognition and words.
- Hippocampal turn (parahippocampal turn): It is a fold that is found on the internal surface of the temporal lobe that borders the hippocampus. The hippocampus circumvolution surrounds the hippocampus and plays an important role in memory.
- Lingual turn: The circumvolution of the occipital lobe that is involved in visual processing. This circumvolution is surrounded by the Calcarino groove and the lateral groove. The lingual circumvolution is adjacent to the parahypocampic gyr.
Circunvolutions and fissures are very important parts of the central nervous system (CNS). The folds of the cerebral cortex creates these turns and furrows that serve to separate brain regions and increase cognitive capacity.
- « 100 phrases about disappointment and disappointment
- Long -term love relationships and the prohibited fruit hypothesis »

