Aroual or Cortical Activation and the Yerkes-Dodson Law

- 2809
- 367
- John Von
A certain amount of stress is necessary in our lives, when their levels are healthy, it represents part of the human adaptation process, primordial for survival, since it prepares and stimulates the body to respond to stimuli and put into action. Adequate stress levels are needed so that the body can perform its functions appropriately.
Content
Toggle- What is the arousal?
- Cortical or arousal activation theory
- Yerkes-Dodson Law
- Eustress and distress
- The Yerkes & Dodson Law in different areas
- Three recommendations to maintain optimal arousal levels
- Conclusion
- Links
- Bibliographic references
What is the arousal?
"It is a physiological and psychological general activation of the organism, which varies in a continuum that goes from deep sleep to intense excitement". GOUL & KRAAN, 1992.
The “Aroual” construct is a term that corresponds to the level of cortical activation which is regulated by the ascending reticular activation system (SARA), when the level of excitation and activation is very high can indicate distress or "negative stress", When it increases until the person begins to experience greater anxiety states, anguish or panic attacks, they are reflected in a decrease in effectiveness in their performance.
Cortical excitability is a measure of the response of the Cortex to stimulation. There is great cortical activation when we are on alert, or in “vigil”, which allows us to perform several mental and physical operations, The high demand in the state of vigil increases the cortical activity of neurons.
Cortical hyperactivation manifests when we experience very intense emotions, stress, anxiety states, also includes panic states. On the other hand, during sleep or relaxation states, cortical activation is smaller.
There is a causal link between the basic dimensions of the personality and neurobiology of the brain, there is a differentiation between the cortical responses that the extraverted ones have with respect to that of the introverts. As Eysenck showed in his personality theory, thus establishing the neurobiological bases of certain stimuli and their responses in cortical centers. It is worth mentioning that the deterioration of performance is different for each personality type mentioned above.
Cortical or arousal activation theory
"A greater cortical or arousal activation, greater physiological reactivity as well as motor activity, and vice versa".
When there is greater cortical activation, the individual has the ability to produce responses and movements more agilely, however When they exceed optimal levels, performance, performance and motivation tend to decline, because the person cannot continue with the same pace he carried, so it is important to learn to Modulate anxiety and stress levels.
Cortical hyperactivation in the body is manifested through great activity by the autonomic nervous system (SNA) in its sympathetic division. Thus experiencing, alterations in the homeostasis control systems or internal balance of the organism, such as: pupila dilation and increased heart rate, to mention some. The relationship between histaminergic axons, cholinergic nuclei in the prosentephalo and trunk are substantial for cortical activation.

The posterior hypothalamus plays an important role in the vigil. Histaminergic neurons constitute one of the sources of excitation for cortical activation during vigil states, especially when a high level of attention is required, and remain calm during sleep.
Yerkes-Dodson Law
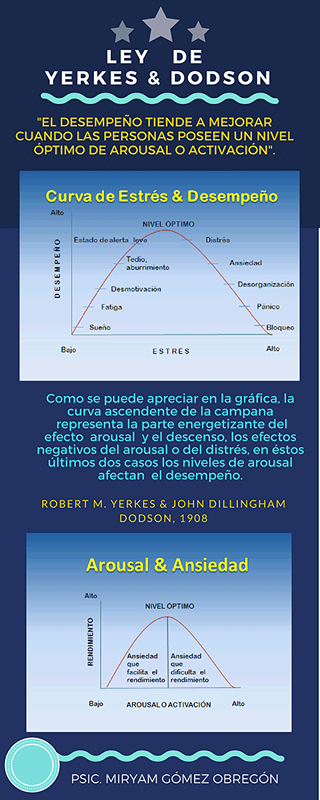
The Yerkes and Dodson Law affirms that performance tends to improve when people have an optimal level of arousal or activation, on the other hand, when the level exceeds or is located below it, in both cases the performance, tends to decline significantly.
Graphically it is represented by means of a bell -shaped curve or an inverted "U". This law was proposed by Robert M. Yerkes and John Dillingham Dodson (1908), It has its neurobiological base in cortical activation and the influence it has on performance. The investigation has shown that in the different activities that we carry out the arousal levels necessary for optimal performance, Each individual has an optimal level of activation. As can be seen in the graphics, lA ascending curve of the bell represents the energetizing part of the Aroual effect And the decrease is caused by the negative effects of the distress, in both cases, arousal levels affect the performance of cognitive processes such as attention, memory, learning, problem solving and decision making, among others.
The brain, to adapt and protect ourselves as a "detector of threats and dangers". When you have a very big concern, so much that you cannot "take it out of your head", that subtracts attention and energy from other tasks that you have to perform throughout the day, sometimes it can affect the progress of other pending activities, since The brain seeks to survive, so it responds first to the dangers. When the threat, whether real or perceived, makes arousal levels exceed optimal, then the proper functioning will decrease.
Eustress and distress
Does stress always have negative effects on people? When the stress and concern you feel motivate you to prepare and study to present a project, for example, at the end of doing so, you can experience a certain degree of satisfaction, this is known as "positive stress" or Eustress. Same that can sharpen your memory, in turn, causes adrenaline, which adds energy that is necessary to complete with your tasks and duties just before you have to deliver them. For that reason, sometimes the last hours are the most productive.
How can pathological anxiety and stress on productivity and performance affect? When there is an excess of anguish and stress, some cognitive skills can be affected or to detriment, such as attention, logical and creative thinking, as well as learning and motivation, among others, it has been observed that it greatly affects in making decisions.
By lasting the states of anxiety and stress or that exceed the optimal levels of activation for a long time, This has a harmful effect on the lives of people and neurologically corresponds to a physiological activation response that is not adaptable to the circumstances that are experienced, thus, the levels of performance, attention, motivational and productivity of the individual can go to detriment; There are people who live under that yoke constantly and for a long time, it is when it becomes chronic producing a negative impact on people's lives.
 Allport's social facilitation theory
Allport's social facilitation theory The Yerkes & Dodson Law in different areas
Apply the law of Yerkes and Dodson can improve performance in the different areas in which the person interacts as could be: academic, sports, business and even inside the home. It is important to identify the levels of stress and motivation that a person can reach and not exceed the difficulty of the tasks that the individual does so that his performance does not decay.
The healthy body seeks homeostasis, being in the just medium corresponds to the optimal levels of performance and balance, When there is a fair measure between healthy motivation and stress, there is an answer that helps adapt and have an adequate coping of the situation, either at home, at school or in the task we do.
In the organizational area, the knowledge of the Yerkes and Dodson Law can be a valuable resource, since excess stress and anxiety generally influences the productivity and performance of workers negatively. When you want to achieve good levels of productivity within the company or organization there must be a work environment that motivates employees and they are recognized in some way when their performance is good.
The arousal "Provides energy ”to be able to perform physical activities, From moderate to intense as in the case of extreme sports and those that require great specific motor demands according to the physical activity carried out.
"Tasks that require persistence can be done better with high levels of Arouse to increase motivation."
For this reason, many times bosses, teachers and coaches constantly press with obtaining results in a certain period of time, so that performance, performance, motivation, attention in tasks and productivity does not decay.
Academically, by increasing the arousal exceeding the optimal level of the same, due to a very stressful situation for the person, for example, that increase in cortical activation will produce a reduction in the effectiveness of the performance of tasks. On the other hand, emotional balance can increase learning.
There is a correspondence between the optimal levels of motivation on performance and performance. Motor impulses are more easily mobilized than intellectual impulses, since they often require a very complex motivation. Partly, personal characteristics should be taken into account. Libet et al. (1983), showed that The potential change in the brain happens before the subject "mentally decides" which movement or action must undertake, This phenomenon is related to brain alert mechanisms.
Three recommendations to maintain optimal arousal levels
- Autaguration. To maintain a good level of performance in your activities, a key step is to be able to Identify your emotional responses to the stimuli that are presented to you. For this, some autob observation techniques can be put into practice to become aware of your physiological and cognitive reactions. When people are able to identify that levels of stress and anguish begin to exceed their optimal level, it is more feasible that they can apply relaxation and breathing techniques in order to modulate those states, facing situations with a more adaptable response and functional.
- Physical activity. Performing a sport or physical activity that you enjoy, at least 5 times per week for 30 consecutive minutes, can bring great benefits for your body and mind, can help you reduce anxiety levels, while contributing to a feeling of general well-being.
- Psychotherapeutic support. When your efforts are not enough to regulate your states of distress and anxiety, you can seek psychological assistance, in this type of space you can learn techniques to handle stress, anxiety and if necessary, you can refer to other professionals from health.
Conclusion
Excessive distress and anxiety can generate behaviors, emotions and cognitions that can fall into dysfunction, be little adaptive or inconvenience; Some of the reactions related to the distress at the cortical level are manifested by difficulty in making decisions, to focus attention, due to sleep and fatigue alterations among many other factors that may have a correlation with the decrease in performance. Hence ands need to ensure balance when you want to have a quality of life, Learn to properly manage stress and anxiety, to modulate them at optimal levels in case it is required, to improve or maintain the performance, productivity and performance of several tasks that we execute in the different areas of our life.
Links
- Recognition and Allegation of Pain and Distress in Laboratory Animals (1992), Institute for Laboratory Animal Research, National Research Council
- https: // www.NAP.Edu/Read/1542/Chapter/2#4
- https: // pubmed.NCBI.NLM.NIH.GOV/17210278/
- https: // www.Researchgate.NET/PUBLICATION/297217568_ENCENACIÓN_EN_CANCH
Bibliographic references
- Tamorri, Stefano, (1990). Neurosciences and sport. Sports Psychology. Mental athlete processes. Barcelona: Paidotribo Editorial.
- Vallejo Ruiloba, J. (1992). Introduction to psychopathology and psychiatry. Mexico: Salvat.
- Nuñez Alonso, J.L. and Martín-Albo Lucas, J. (2004). Competition Psychology. Seville: Wanceulen, Sports Editorial. S.L.

