Alcohol consumption effects, risk and dependence

- 1928
- 475
- Austin Stokes
Between the Drugs classified as depressing of the central nervous system, are alcoholic beverages. Alcohol is a substance that is found in fermented drinks such as wine, beer, cider and others, or in distillates such as brandy, rum, cognac, gin, whiskey, etc. The alcohol content is not the same in all drinks and is indicated by the alcoholic degree, for example, 12º means that in 1000 ml of drink there are 120 ml of ethyl alcohol of 96º.
Content
Toggle- The alcoholism
- Alcohol in Spain
- Consumption effects
- What is risk consumption?
- Pathologies associated with alcoholism
- Alcohol psychosocial consequences
- How to abandon alcohol consumption?
- Some of the ways to face the abandonment of consumption are:
- Stop drinking improves the quality of life:
- Bibliography
The alcoholism
Alcoholism is a viro-metabolic disease conditioned by the continuous exposure of the body to alcohol. It is characterized by the insatiable desire to drink this substance, loss of control so as not to continue drinking after it begins, physical dependence or appearance of symptoms after abstinence, and tolerance or need to increase the amount of alcohol ingested.
Many times the activities of the person revolve around the substance; It is possible that you spend a lot of time to achieve it, take it and recover from its effects. And despite seeing the consequences, both physical and psychological that causes consumption, continues to consume it.
There is an enzyme in the body responsible for destroying alcohol called aldehyde dehydrogenase, but not all people possess them equally. In the man we can find it in two places, first in the mucosa of the stomach and then in the liver, instead the woman only has this enzyme in the liver, she does not have in the stomach or, in any case, she is in a percentage 80 times lower.
A man can absorb 25% of the alcohol that consumes in the stomach, while the woman does not, so it is less resistant to their effects. Once in the liver the alcohol is metabolized, generating other substances also toxic to the body.
All alcohol that the liver is not able to absorb passes to the blood (breathalyzer) And from there it goes directly to the brain, affecting the central nervous system. There are some strange cases in which the person does not have dehydrogenase in his body, are those individuals to whom alcohol feels bad, producing nausea, diarrhea, heat, blush, etc. so they can't take it.

Alcohol in Spain
It is possible. The cirrhotic disease rate in Spain is also much higher, of 24 people for every one hundred thousand inhabitants, and in Sweden it is in two people of every one hundred thousand.
A person, After a year of drinking alcohol in large quantities already presents psychic and physical dependence.
Consumption effects
With moderate consumption, the main effects are the feeling of relaxation, liberation and increase in self -confidence, loquacity, decreased attention and euphoria. As the quantity increases all these symptoms are accentuated negatively.
A is adopted speech incongruous, lack of movements and balance coordination, Loss of reflexes and even knowledge, producing intoxication or intoxication, with agitation, diplopia (see double) and risk of respiratory arrest. In addition, each gram of alcohol contains 7 kcal, which accumulate in the form of fat in most people, causing an overweight.
 Alcoholic neuropathy: symptoms, causes and treatment
Alcoholic neuropathy: symptoms, causes and treatment What is risk consumption?
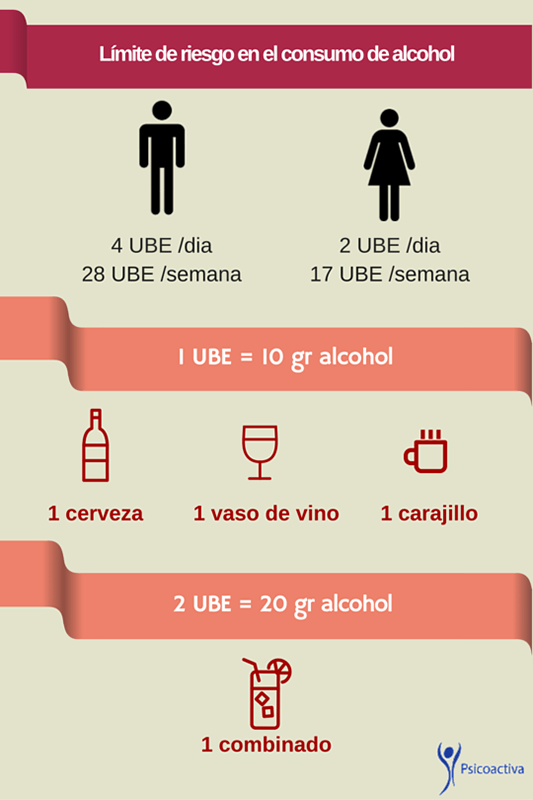
To define whether or not there is a risk consumption is measured in Beverage Estandard Units (UBE):
Pathologies associated with alcoholism
The initial characteristics of this disease are the lack of appetite, sleep disorders, hypertension, anemia, sexual impotence, hand tremor, diarrhea, etc.
In the long term, it produces different associated pathologies such as gastritis, gastrointestinal ulcers, liver disorders (hepatitis and cirrhosis), 80% of all chronic pancreatitis and almost all acute. It also causes a vitamin B1 deficit and affects the red manufacturing mechanism, especially lymphocytes, so addicts usually suffer from more infectious diseases. This list is thickened with cardiovascular, neurological, dementias and alcoholic psychosis alterations.
Alcohol is a brain depressant, although it produces euphoria symptoms. When it reaches the brain, what is most affected is the cortex area, the most characteristic part that humans possess and the most developed. The higher the dose of alcohol, the more structural areas of the brain are affected, and that is what produces the final depression, so dangerous for the body.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome are a set of symptoms that appear due to cessation or reduction in consumption. These occur after a prolonged period of large alcohol intakes and you can develop hours or days after the interruption: morning discomfort, extremities, tongue and even face, anxiety, sweating, insomnia, nausea, vomiting and visual hallucinations (usually be related to insects and can last several days), in very extreme cases the delirium tremens occurs, which can cause death.
Alcohol psychosocial consequences
At a family level, psychosocial consequences are characterized by greater irritability by the patient, which encourages the appearance of fights, ill -treatment, abandonment of the family and even separation.
As for the social level we can observe a loss of relations, the appearance of legal-legal problems, altercations, recklessness and accidents.
In work there can be absenteeism when alcoholism is already very established, decrease in performance, work accidents, low and layoffs.
 Cocaine: History, composition and side effects
Cocaine: History, composition and side effects How to abandon alcohol consumption?
Medical treatment must begin with detoxification, which can be outpatient or even hospitable. After preventing alcohol consumption, reassuring are usually administered to reduce anxiety produced by withdrawal syndrome, called benzodiazepines during the first days.
Subsequently, abstinence must be maintained through alcoholic uninhabiting, other medications are administered for this, that prevent drinking once again has stopped consuming. Individual and group therapies of psychological aid are also performed, as well as follow -up visits.
Some of the ways to face the abandonment of consumption are:
- Rehearsing different ways to reject the offer: "No, thanks, I'm taking medications ...".
- Remembering the list of reasoning you don't drink for is the best option.
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep and leisurely breathing.
- Wait a few minutes to pass the desire.
- Distract with activities that occupy time.
- To think that alcohol does not solve problems, on the contrary, prevents clearly thinking.
Stop drinking improves the quality of life:
There are many benefits of abandoning alcohol consumption, such as having greater mental agility, an increase in physical well -being, more appetite, enjoying better humor, driving more safely, saving money, greater concentration and performance at work, and Increased self -esteem.
Bibliography
- Belloch, a., Sandín, b., Ramos, f. (1995): Psychopathology Manual. Spain. McGraw-Hill.
- Cie 10, mental and behavioral disorders. Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. (1992) World Health Organization. Madrid. Mediator.
- DSM-V, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders.
- Steinglass, p., Bennet, l. TO., Wolin, s. J., Reiss, d. (1997): The alcoholic family. Barcelona. Gedisa.

